Protein Glycosylation

Cell Biology Glossary N Linked Glycosylation Draw It To Know It
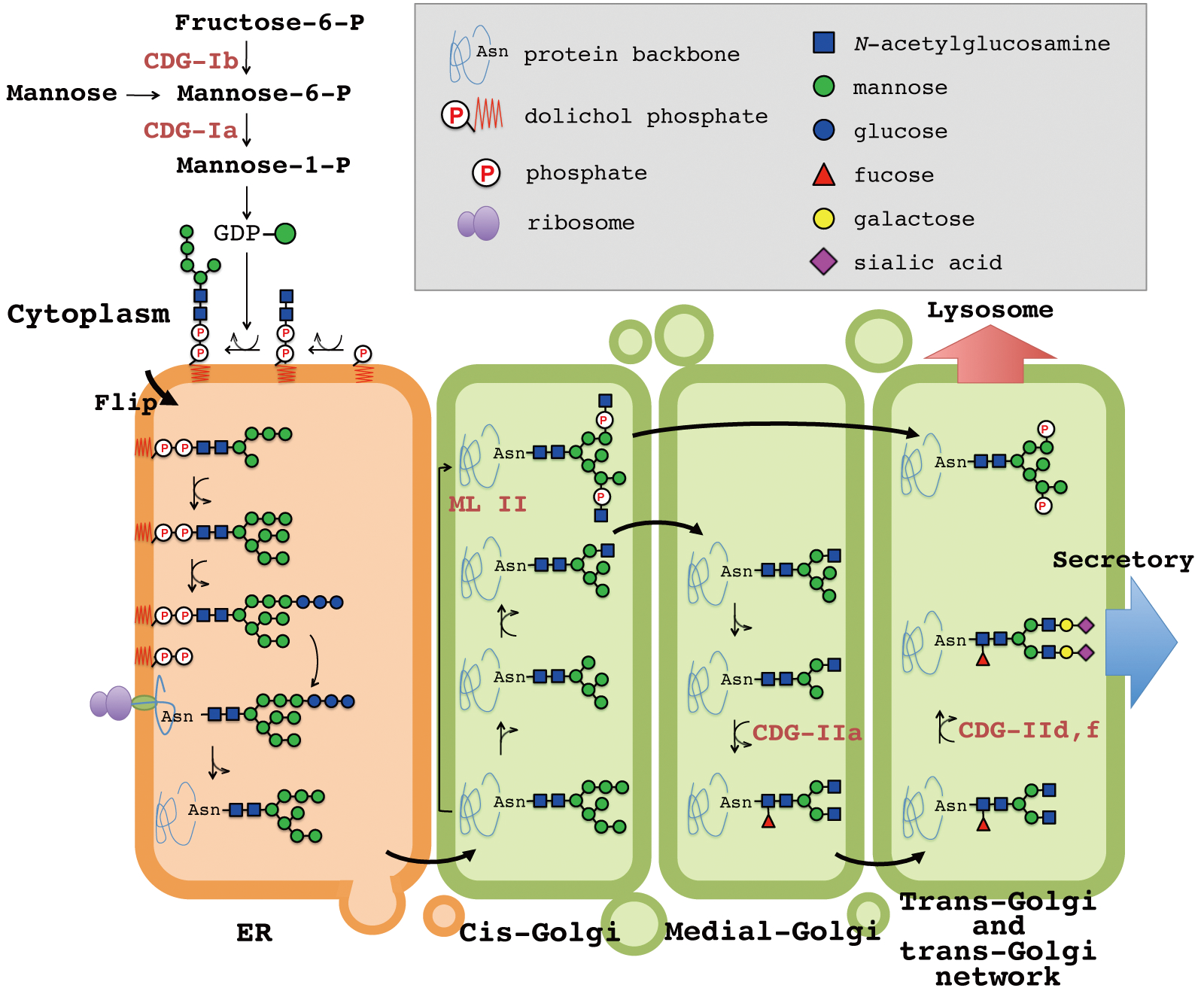
Genetic Diseases Associated With Protein Glycosylation Disorders In Mammals Intechopen

15
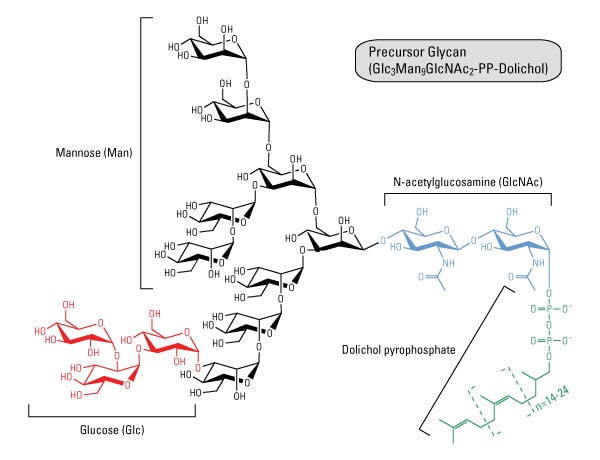
Glycosylation Thermo Fisher Scientific Us
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsvmtt2orbeoyiq3rp 1jbdv Fiuiexhbjabeykz6u2igzb9a Usqp Cau
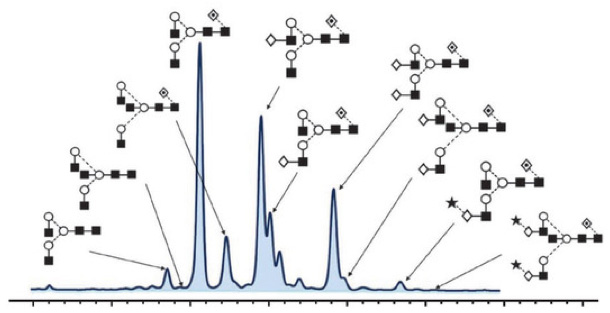
Protein Glycosylation Creative Proteomics
Glycosylation is a type of post-translational modification of the protein that occurs in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.

Protein glycosylation. The βc protein contains an N-linked glycosylation site at Asn 328. Glycosylated proteins are then transported to different cellular locations through the Golgi complex. Protein glycosylation helps in proper folding of proteins, stability and in cell to cell adhesion commonly needed by cells of the immune system.
Occurs after a protein enters the ER. Glycosylation is critical for a wide range of biological processes, including the attachment of cell to the extracellular matrix and intracellular protein-ligand interactions. Glycosylation is a very common posttranslational modification and occurs by the actions of an array of glycosyltransferase enzymes.
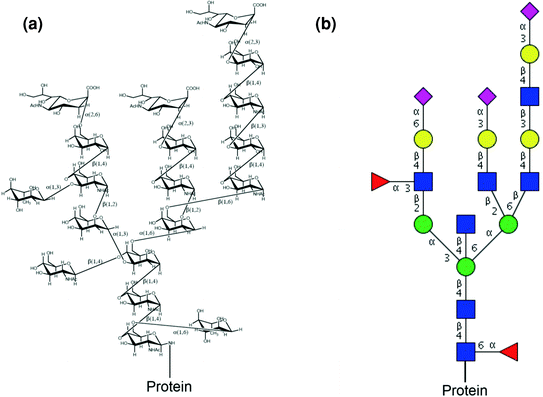
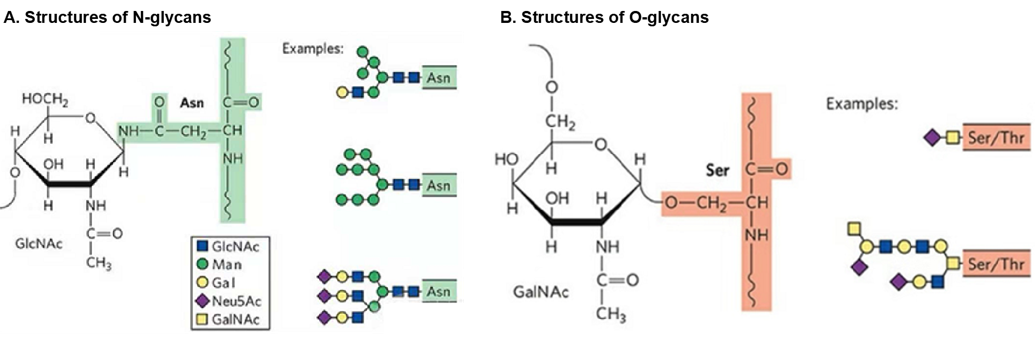
Protein glycosylation is the covalent attachment of single sugars or glycans, i.e., multi-sugar polysaccharides or complex oligosaccharides, to select residues of target proteins. Protein glycosylation is an essential co- and post-translational modification of secretory and membrane proteins in all eukaryotes. Eichler introduces the diversity of protein glycosylations and the roles of these modifications in regulating protein function.
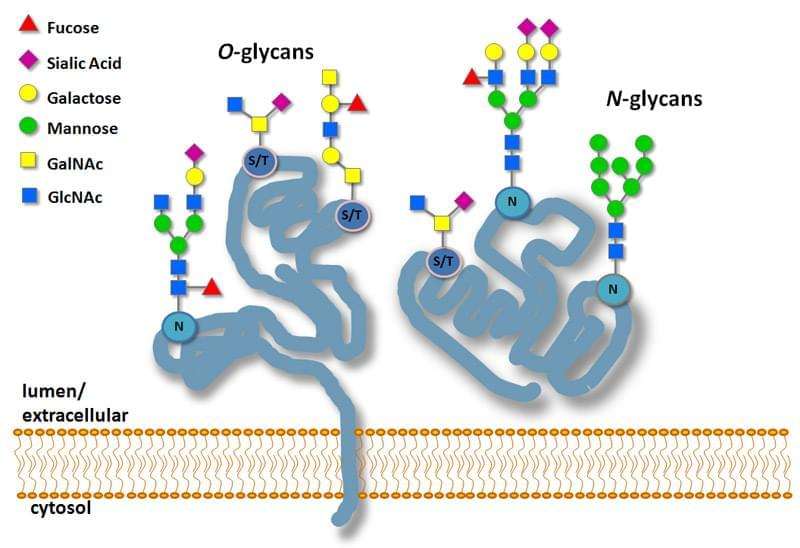
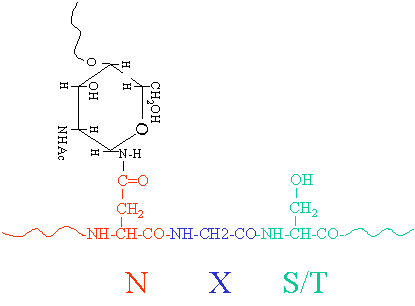
The initial steps of N-glycosylation and N-glycan processing are highly conserved between plants, mammals and yeast. N-linked glycosylation occurs via a complex and integrated sequence of enzymatic transformations that result first in the assembly of a key membrane-bound polyprenyl-pyrophosphate-linked glycosyl donor. It refers to the attachment of glycans to serine and threonine, and, to a lesser extent, to hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine.
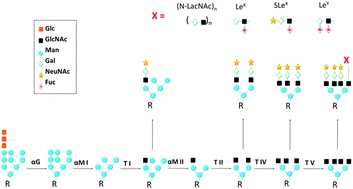
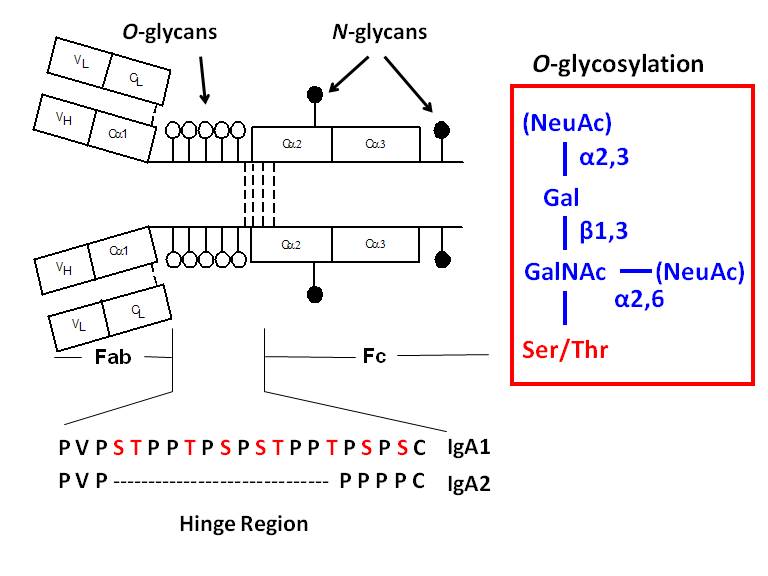
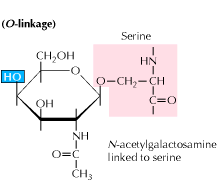
Proteins may be glycosylated at multiple sites with glycans, and the most common forms of glycosylation are N-linked and O-linked glycosylation. Begins in the ER and continues in the golgi. Cell surface and extracellular proteins are O-glycosylated, where the most abundant type of O-glycosylation in proteins is the GalNAc attachment to serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) in the protein chain by an a-glycosidic linkage.
Even in highly glycosylated proteins though, the sugar residues often acts as recognition sites for other cells. Glycosylation is the most common post-translational modification of proteins in eukaryotic cells. N-linked Protein Glycosylation Begins in the ER;.
O-linked glycosylation of secreted and membrane bound proteins is a post-translational event that takes place in the cis-Golgi compartment after N-glycosylation and folding of the protein. Glycosylation is a complex form of protein modification occurring in the secretory pathway. Studies on viral glycosylation are often limited to analysis of recombinant proteins that in most cases are produced in cell lines with a glycosylation capacity different from the capacity of the host cells.
Glycosylation refers to the attachment of sugars to proteins, a normal process required for the healthy function of cells. Disorders of protein n-glycosylation Most subtypes of CDG are classified as disorders of N-glycosylation, which involves carbohydrates called N-linked oligosaccharides. Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to amino acid side-chains.
This process is known as glycosylation. Neoplastic transformation results in a wide variety of cellular alterations that impact the growth, survival, and general behavior of affected tissue. Protein Glycosylation O-linked Glycosylation.
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially through the catalytic action of certain enzymes Supplement In general, glycosylation is a chemical reaction where a carbohydrate (a glycosyl donor) is attached to the hydroxyl or other functional group of a glycosyl acceptor. Glycans assist in protein folding and help the virus avoid immune recognition by the host. Although genetic alterations underpin the development of neoplastic disease, epigenetic changes can exert an equally significant effect on neoplastic transformation.
Protein Glycosylation begins with an overview of the chemical structures of mono- and oligosaccharides, to provide a scientific basis for the later chapters. This process determines the destiny of the proteins to which a sugar chain (glycoproteins) has been added, which will be secreted or will form part of the cellular surface, as in the case of the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP). Even though O-glycosylation has been expected on the spike protein of SARS-Cov-2, this is the first report of the site of O-glycosylation and identity of the O-glycans attached on the subunit S1.
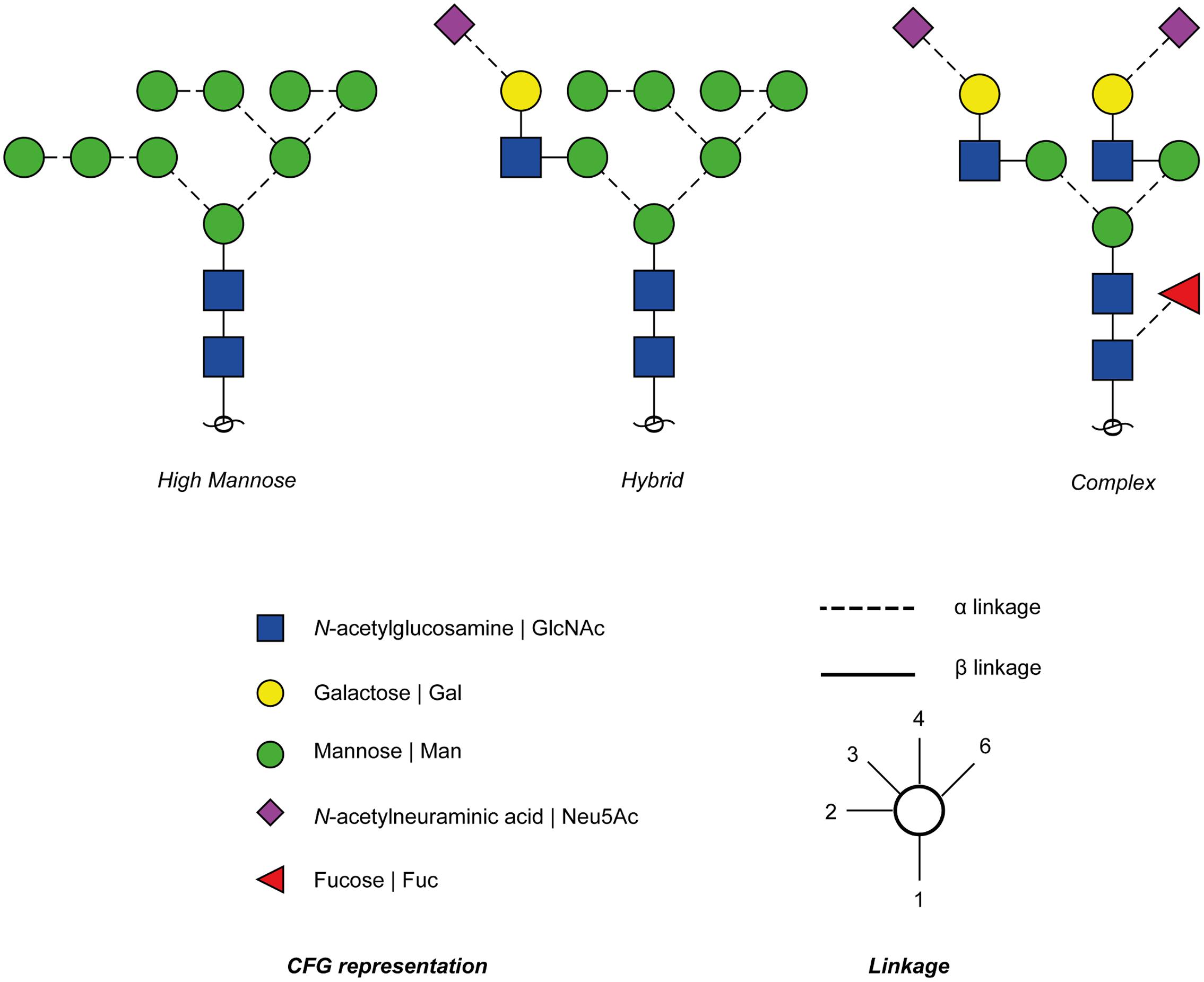
Glycosylation of the proteins to form a glycoprotein is necessary for different biological purposes. Because glycosylation regulates a wide range of activities in cells throughout the body, defects in glycosylation can cause extensive and severe symptoms. The addition of N - and O -glycans affects intracellular processes like the folding and trafficking of most glycoproteins.
Intracellular protein O-glycosylation likely functions as a nutrient sensor providing a biochemical switch to enable the cell to adapt its physiology depending upon the presence of low, normal, or high glucose levels. Often, multiple forms of the protein are observed, with indiscrete higher molecular weight bands due to the presence of multiple glycosylated forms. Altered glycans on the tumor- and host-cell surface and in the tumor microenvironment have been identified to mediate critical events in cancer pathogenesis and progression.
In contrast, late N-glycan maturation steps in the …. As one of the most important recognition signals, glycosylated proteins and peptides are involved in much intracellular communication, such as apoptosis, cell growth regulation, infection process, and immunological differentiation. Glycosylation can impact how cells communicate, respond to their environment, grow and function.
Protein glycosylation Curr Biol. Glycosylation is a ubiquitous modification that occurs on proteins and lipids in all living cells. The viral proteins produced in an infected cell undergo the 'glycosylation' and then pass through the quality control steps, which involves 'trimming' by an enzyme called 'MANEA'.
Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. A variety of proteins are postranslationally modified with clustered sites of O-glycosylation. This protein interacts with a number of cytokine receptors including IL5, interleukin 3 (IL3) and granulocyte-macrophage colony- stimulating factor (GM-CSF).
Glycosylation is one of the most abundant posttranslation modifications of proteins, and accumulating evidence indicate that the vast majority of proteins in eukaryotes are glycosylated. Protein N-glycosylation plays critical roles in controlling brain function, but little is known about human brain N-glycoproteome and its alterations in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The glycosylation pattern of the produced recombinant glycoproteins might therefore be different from the pattern on native viral proteins.
Most eukaryotic nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins modified by a-linked O …. Glycosidic bond —the site of glycan linkage Glycan composition—the types of sugars that are linked to a given protein Glycan structure—can be unbranched or branched chains of. Thus, by regulating protein activity, glycosylation is involved in the normal functioning.
Protein glycosylation is a complex posttranslational modification that manipulates the biological activity and function of therapeutic glycoproteins. Protein glycosylation has multiple functions in the cell. O-linked glycosylation is the attachment of a sugar molecule to the oxygen atom of serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues in a protein.
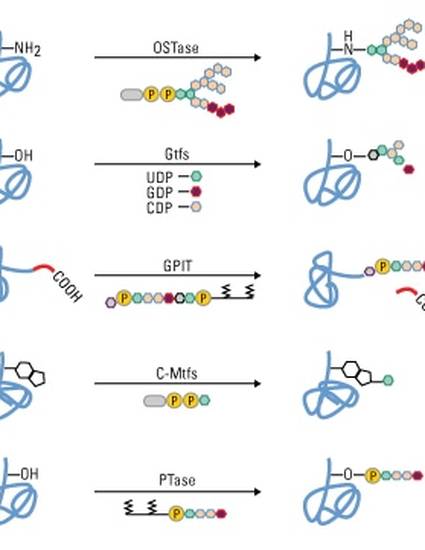
Speak to a specialist. These oligosaccharides are created in a specific order to create specific sugar trees, which are then attached to proteins on various cells. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification.
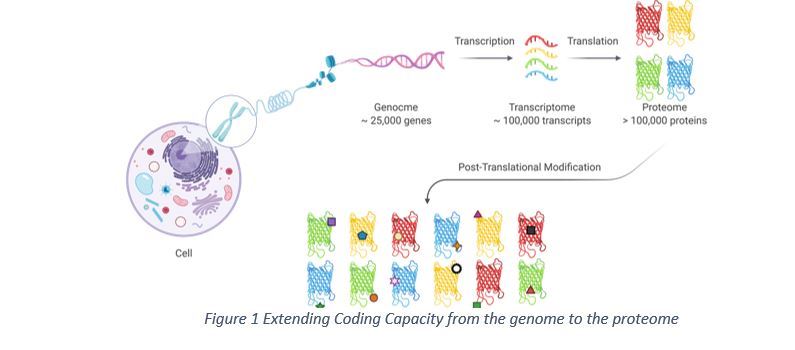
Protein Glycosylation is the post-translational process by which saccharides are selectively added to specific protein residues utilizing two distinct mechanisms in order to convey more structural stability or function to the native protein structure. Protein glycosylation typically leads to a diverse array of product glycans due to multiple factors. Glycosylation increases diversity in the proteome, because almost every aspect of glycosylation can be modified, including:.
Here, we report the first, large-scale, site-specific N-glycoproteome profiling study of human AD and control brains using mass spectrometry–based quantitative N-glycoproteomics. Protein glycosylation is a fundamental process in nature that controls essential biological pathways, ranging from protein trafficking and cell adhesion to host–pathogen interactions. Simply, glycosylation occurs when sugar molecules (glucose) floating around in our blood attach to protein molecules, diminishing their effectiveness and causing inflammation.
As one of the more common yet most complex post-translational modifications, protein glycosylation not only greatly contributes to the. Glycosylation, the attachment of sugar moieties to proteins, is a post-translational modification (PTM) that provides greater proteomic diversity than other PTMs. This process, which increases as we age, happens so readily that it doesn't even require a specific enzyme to push it ahead.
Glycosylation is the process or result of addition of saccharides to proteins and lipids.The process is one of four principal co-translational and post-translational modification steps in the synthesis of membrane and secreted proteins and the majority of proteins synthesized in the rough ER undergo glycosylation. That's also why glycosylation is so dangerous. What is protein glycosylation?.
Numerous glycoproteins are N-linked. In the ER, glycosylation is used to monitor the status. It is an enzyme-directed site-specific process, as opposed to the non-enzymatic.
Occurs inside the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi complex. The diverse and complex structure of glycans on proteins often directs specific biological processes and when altered can give rise to a variety of diseases. Glycosylated proteins (glycoproteins) are found in almost all living organisms that have been studied,.
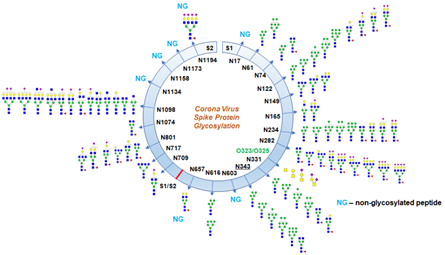
In biochemistry, glycosylation refers to the. In a recent study, spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 were analyzed using mass spec analysis to determine the N-glycosylation profile of the subunits that make up the spike protein. To date, a plethora of functions related to.
The protein is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues with the highest expression in the brain, placenta and pancreas. O-glycosylation is a post-translational modification that occurs after the protein has been synthesised. Aberrant glycosylation of proteins is connected with cell immortalization, transformation, and metastasis.
Glycosylation plays a role in protein folding, interaction, stability, and mobility, as well as in signal transduction. For instance, the zona pellucida is very important as a physical barrier that protects the egg, but glycosylated ZP3 also acts as a sperm receptor. Protein glycosylation is an enzyme-directed chemical reaction that takes place in the ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum) and in the Golgi Apparatus body of the cell.
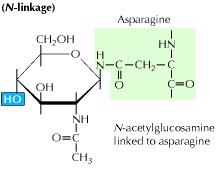
Therefore, the βc protein is a common signal transducing partner to many cytokine receptors. Indeed, the modification of proteins through enzymatic glycosylation is an event that reaches beyond the genome and is controlled by factors that differ greatly among cell types and species. Asparagine-linked (N-linked) glycosylation is an essential protein modification that is associated with all domains of life.
The book includes discussions on the purification, function, and enzyme kinetics of selected glycosidases and glycotransferases, as well as a review of the roles of oligosaccharides in. Among neoplasia-associated epigenetic alterations, changes in cellular. Due to its many biological functions, glycosylation is one of the most-studied PTMs of eukaryotic cell proteins.
G General glycosylation within the ER helps with folding, and glycosylation in the Golgi body tells a protein where to go. Author Jerry Eichler 1 Affiliation. The major sites of protein glycosylation in the body are ER, Golgi body, nucleus and the cell fluid.
Glycosylation is the most complex post-translational modification of proteins. The question of native versus foreign glycosylation in humans is a contentious subject because it is not totally clear what the native glycosylation state is since it can vary so frequently between and even within each species. Glycosylation is usually suspected if a protein contains potential glycosylation sites and migrates slower in a gel than expected based on its predicted molecular weight.
Inside the ER lumen, the protein folds into its characteristic three-dimensional conformation. Abstract Tn syndrome is a rare autoimmune disease in which subpopulations of blood cells in all lineages carry an incompletely glycosylated membrane glycoprotein, known as the Tn antigen. Glycosylation consists of adding carbohydrates to a protein.
This type of linkage is important for both the structure and function of some eukaryotic. Occurs only in the golgi. N-linked glycans are covalently attached to the protein at.
Consistent with their high complexity, glycans play crucial biological roles in protein quality control and recognition events. Tools for Analyzing Glycoproteins.

Engineering Protein Glycosylation In Prokaryotes Sciencedirect

Controlling Glycosylation In Fusion Protein Manufacturing To Generate Potent Biobetters Bioprocess Internationalbioprocess International

Functional Characterization Of Bacterial Oligosaccharyltransferases Involved In O Linked Protein Glycosylation Journal Of Bacteriology

Structural Biochemistry Proteins Protein Glycosylation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
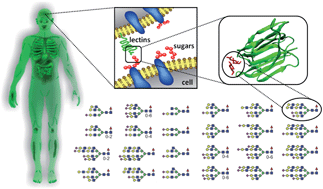
Mammalian Protein Glycosylation Structure Versus Function Analyst Rsc Publishing

N Linked Glycosylation Wikipedia
Protein Glycosylation Study Glycosylation In Proteins Using Simglycan

Sars Cov 2 S Protein Glycosylation

Sequential Glycosylation Of Proteins With Substrate Specific N Glycosyltransferases Acs Cent Sci X Mol

Perturbing The Folding Energy Landscape Of The Bacterial Immunity Protein Im7 By Site Specific N Linked Glycosylation Pnas
Protein Glycosylation And Its Impact On Biotechnology Springerlink
Hupo Glycosylation Is A Common Modification Of Human Proteins
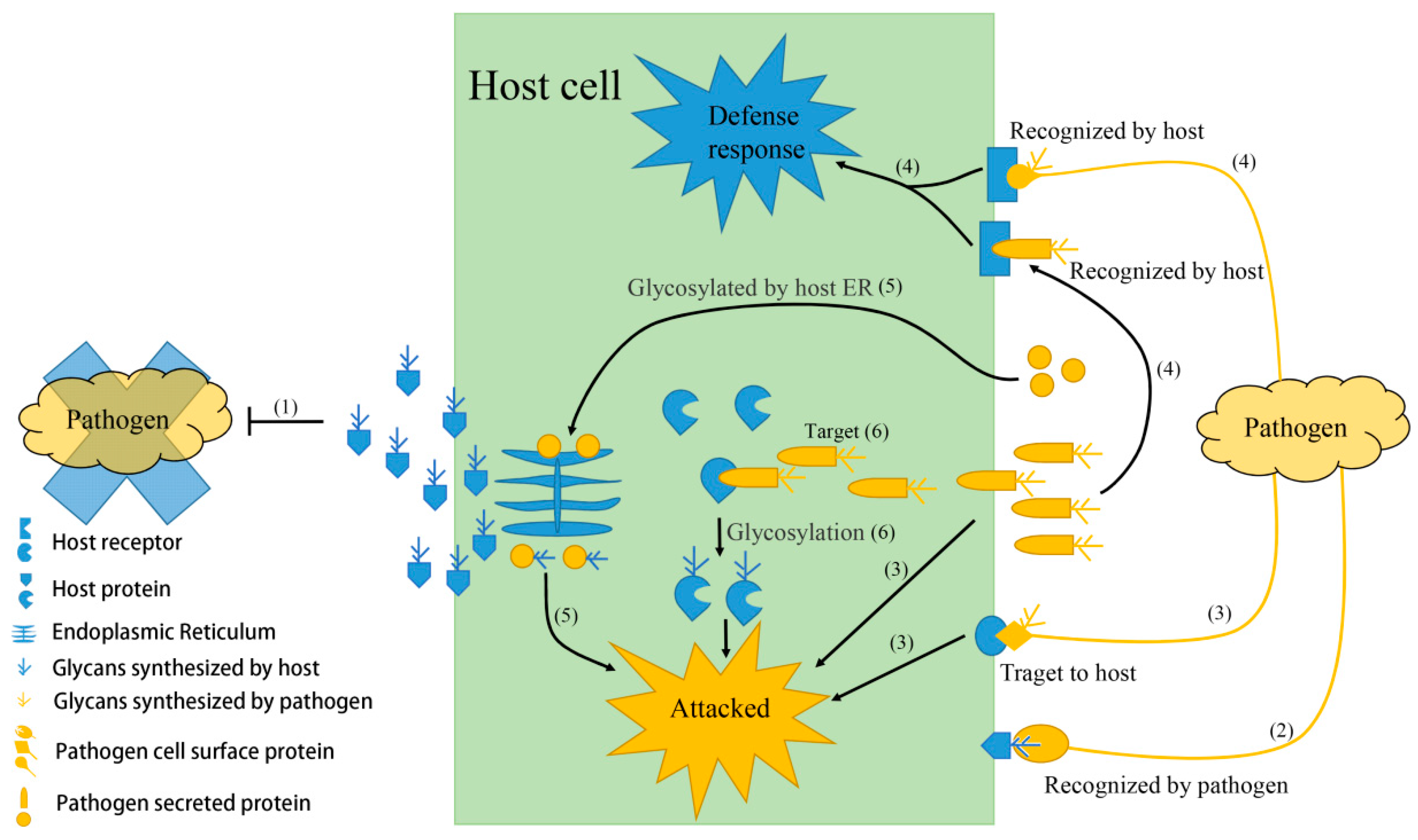
Cells Free Full Text Role Of Protein Glycosylation In Host Pathogen Interaction
Protein Glycosylation An Evolutionary Crossroad Between Genes And Environment Molecular Biosystems Rsc Publishing

Pdf Mechanisms And Principles Of N Linked Protein Glycosylation Semantic Scholar
Flavivirus Envelope Protein Glycosylation Impacts On Viral Infection And Pathogenesis Journal Of Virology
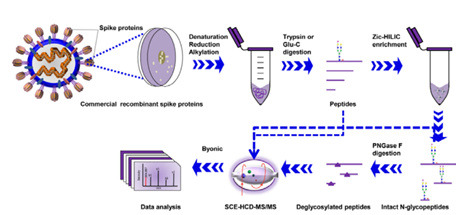
Analysis Of Protein Glycosylation By Mass Spectrometry By Susan Rey

Glycosylation Engineering Of S Layer Proteins For Bioactivity

Sugar Coating Bacterial Protein Glycosylation And Host Microbe Interactions Trends In Biochemical Sciences
Frontiers Dengue Virus Glycosylation What Do We Know Microbiology
Protein Glycosylation

Host Protein Glycosylation In Nucleic Acid Vaccines As A Potential Hurdle In Vaccine Design For Nonviral Pathogens News Break

Identification And Characterization Of Protein Glycosylation Using Specific Endo And Exoglycosidases Semantic Scholar

Intracellular Transport 4 3 Glycosylation Sequences And Protein Glycosylation Openlearn Open University S377 3
1

Protein Glycosylation In Cancer Abstract Europe Pmc
Importance Of Glycosylation In Biological Processes Glycotope
Understanding Genetic Control Of Human Protein N Glycosylation Polyomica
Implications Of Cell Culture Conditions On Protein Glycosylation Biopharm International
Protein Glycosylation

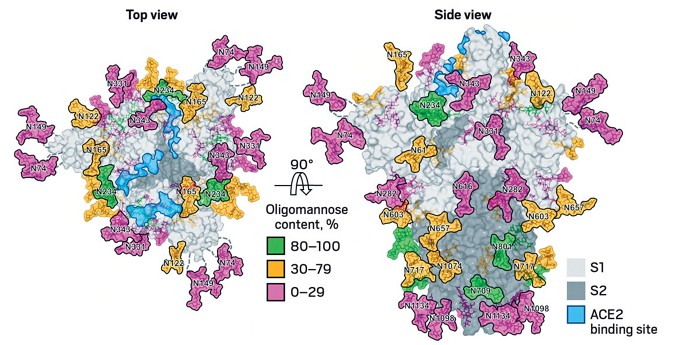
Site Specific Glycan Analysis Of The Sars Cov 2 Spike Science
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsj7npjsvotfguvepommjiakmv2jgn4xr43cfkjbbf Fvanr0ge Usqp Cau

Fucosylation And Protein Glycosylation Create Functional Receptors For Cholera Toxin Elife

Bacterial Glycoengineering As A Biosynthetic Route To Customized Glycomolecules Biorxiv
N Linked Glycosylation And Its Potential Application In Drug Development Insight Medical Publishing

Protein Glycosylation
Protein Glycosylation Labeling Service Creative Biomart

The Glycosylation Of The Complement Regulatory Protein Human Erythrocyte Cd59 Davis Lab Oxford Structure Based Immunology

N Linked And O Linked Protein Glycosylation Occurs In The Er And Golgi Download Scientific Diagram

26 Questions With Answers In Protein Glycosylation Science Topic

Considerations In Controlling Glycosylation Variability In Biosimilar Protein Therapeuticsbioprocess International
Protein Glycosylation Study Glycosylation In Proteins Using Simglycan

Protein Glycosylation In Aspergillus Fumigatus Is Essential For Cell Wall Synthesis And Serves As A Promising Model Of Multicellular Eukaryotic Development

Methods And Matrices For Mass Spectrometry Of Glycans Sigma Aldrich

Customized Protein Glycosylation To Improve Biopharmaceutical Function And Targeting Sciencedirect
Research Development Of Protein Glycosylation
The Art Of Glycosylation Of Sars Cov 2 S Protein Acrobiosystems
Adding The Missing Sugars To Coronavirus Protein Structures
N And O Linked Protein Glycosylation

Qualitative And Quantitative Analyses For Protein Glycosylation Creative Proteomics Blog
Protein Glycosylation Creative Peptides

The Role Of Glycosylation In Receptor Signaling Intechopen

Overview Protein Glycosylation Analysis Proglycan

Mechanisms And Principles Of N Linked Protein Glycosylation Sciencedirect
The Art Of Glycosylation Of Sars Cov 2 S Protein Acrobiosystems
Sweet New Roles For Protein Glycosylation In Prokaryotes Trends In Microbiology
Mass Spectrometry Toolkit For The Characterisation Of Protein Glycosylation Quality Assistance
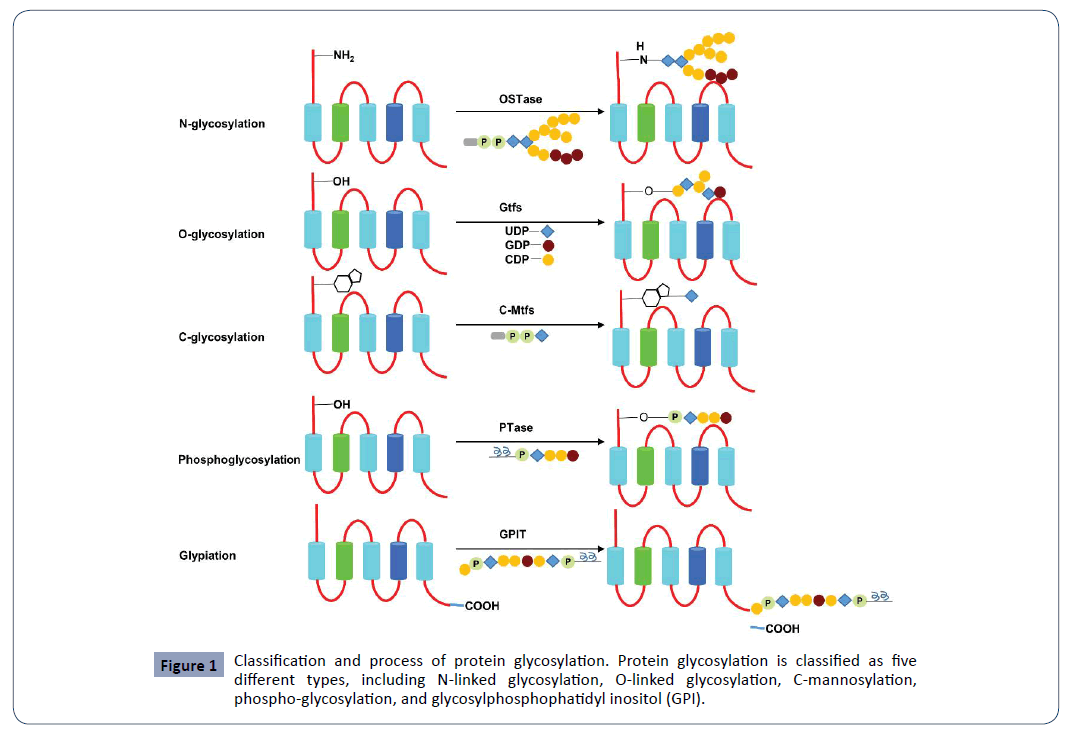
N Linked Glycosylation And Its Potential Application In Drug Development Insight Medical Publishing

Intracellular Transport 4 3 Glycosylation Sequences And Protein Glycosylation Openlearn Open University S377 3
Mass Spectrometry Toolkit For The Characterisation Of Protein Glycosylation Quality Assistance
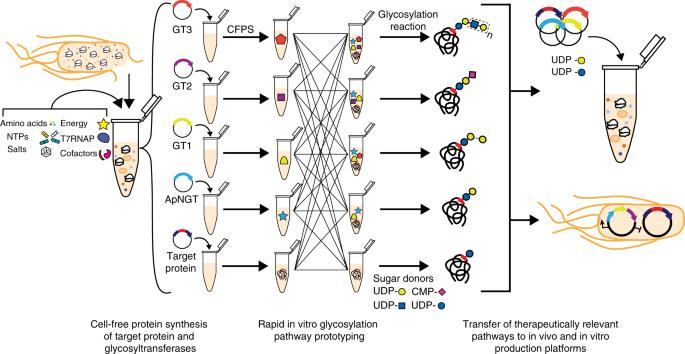
A Cell Free Biosynthesis Platform For Modular Construction Of Protein Glycosylation Pathways Nature Communications
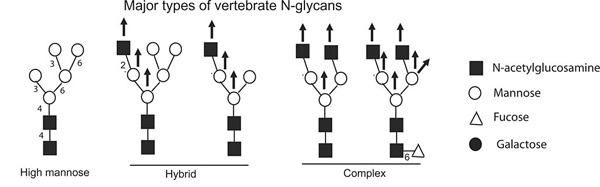
Prion Protein N Linked Glycosylation Review And Assessment Of Therapeutic Potential

Protein Glycosylation In Cancer Abstract Europe Pmc
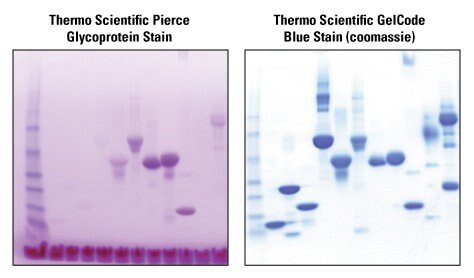
Glycosylation Thermo Fisher Scientific Us
Diseases Of Protein Glycosylation Nuffield Department Of Clinical Neurosciences
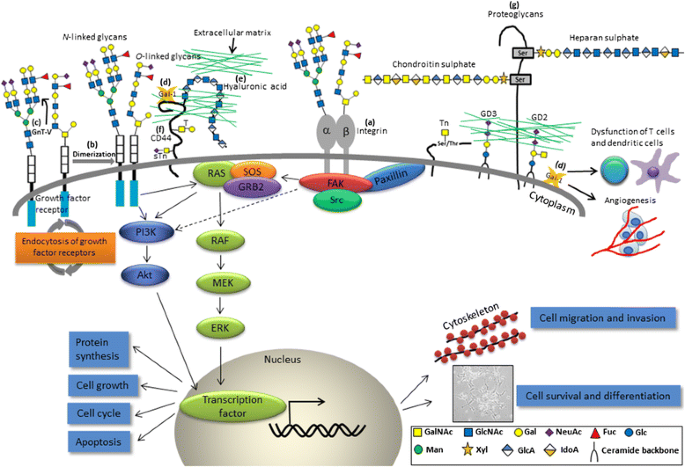
Protein Glycosylation In Cancers And Its Potential Therapeutic Applications In Neuroblastoma Springerlink
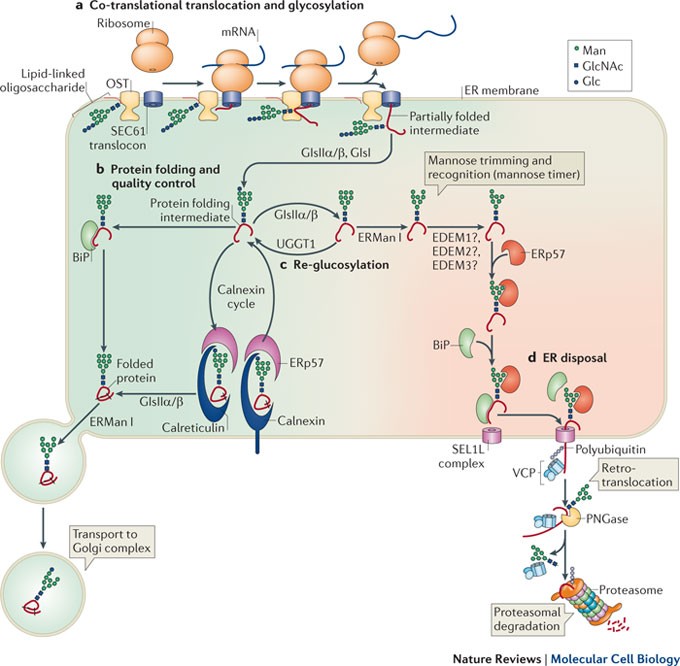
Vertebrate Protein Glycosylation Diversity Synthesis And Function Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

Effect Of Glycosylation On Protein Folding A Close Look At Thermodynamic Stabilization Pnas

In Vitro Glycosylation Jewett Lab

Characterization Of Protein Glycosylation Using Esi Chiptm Static Nanospray Iontrap Msn Mass Spectrometry

Protein Folding And Glycosylation In The Endoplasmic Reticulum Draw It To Know It

Glyco What International Milk Genomics Consortium
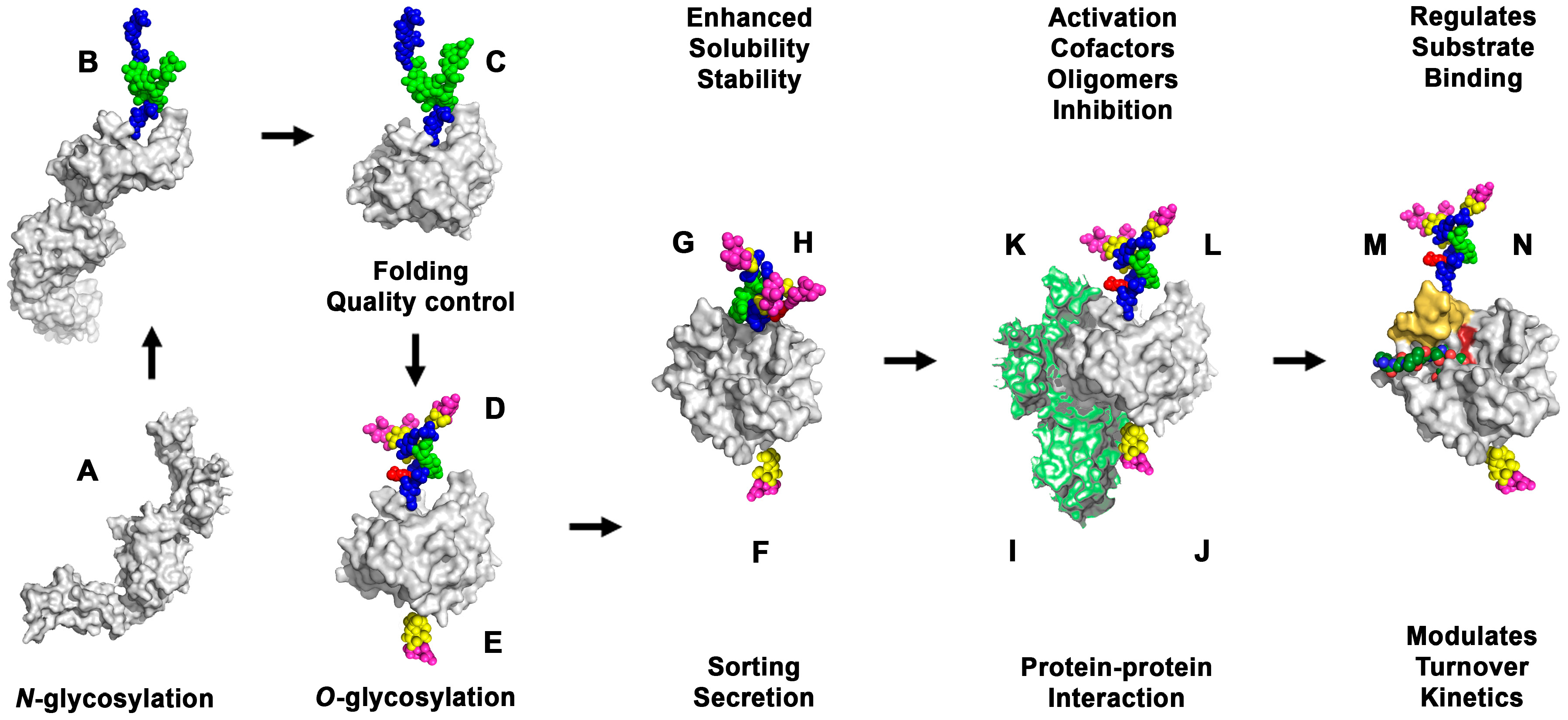
Ijms Free Full Text Effects Of Glycosylation On The Enzymatic Activity And Mechanisms Of Proteases Html
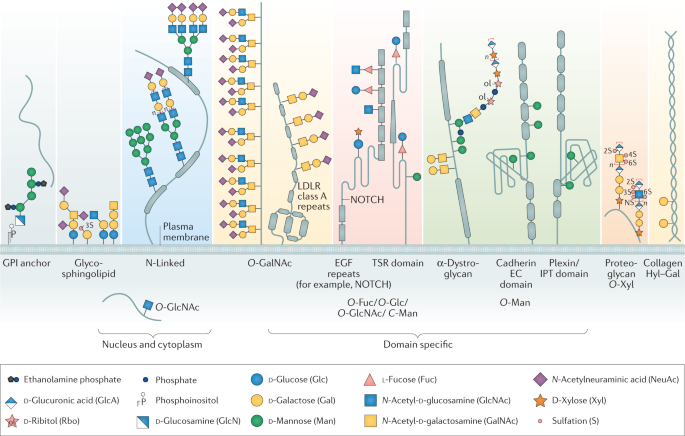
Global View Of Human Protein Glycosylation Pathways And Functions Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

April 14 Surreal Science Stuff

N Linked Glycosylation Youtube
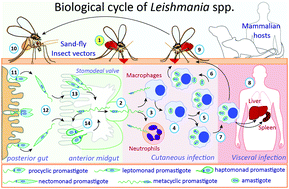
Protein Glycosylation In Leishmania Spp Molecular Omics Rsc Publishing

Multiple Reaction Monitoring For The Quantitation Of Serum Protein Glycosylation Profiles Application To Ovarian Cancer J Proteome Res X Mol

Brief Discussion On Protein Glycosylation By Array Glycan Issuu
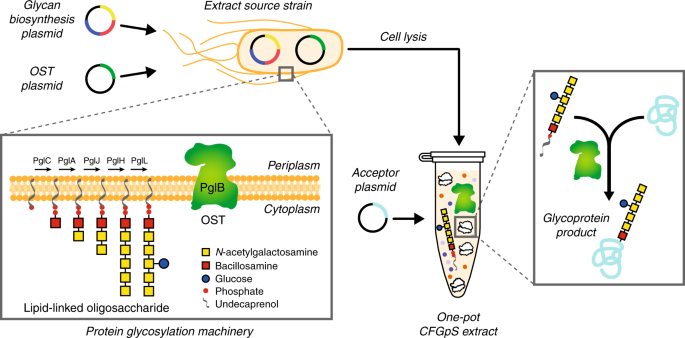
Single Pot Glycoprotein Biosynthesis Using A Cell Free Transcription Translation System Enriched With Glycosylation Machinery Nature Communications

Glycosylation Overview And How To Control Glycosylation Using In Vitro Glycoengineering Cell Culture Dish
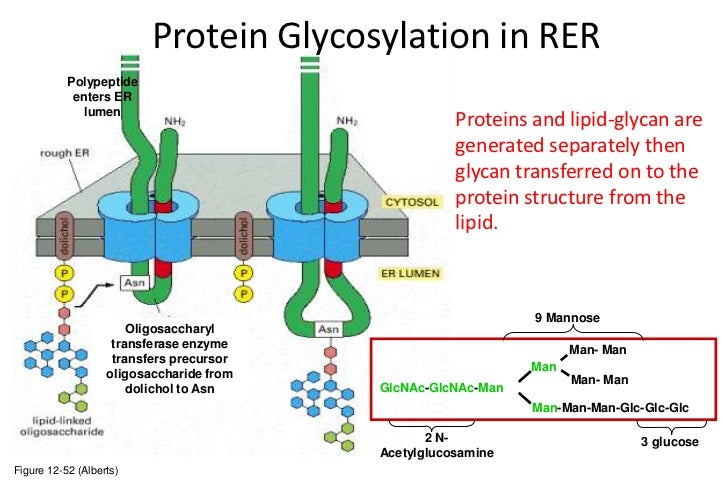
Lecture 7 Glycosylation In Cell Culture
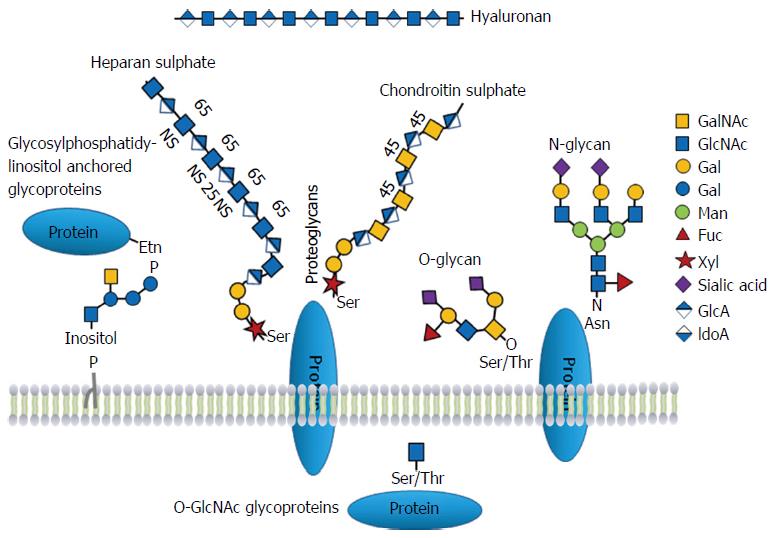
Glycoproteins And Glycoproteomics In Pancreatic Cancer

Protein Glycosylation An Important Tool For Diagnosis Or Early Detection Of Diseases Sciencedirect

Alteration Of Brain Glycoproteins During Aging Sato 10 Geriatrics Amp Gerontology International Wiley Online Library

Vulnerabilities In Coronavirus Glycan Shields Despite Extensive Glycosylation Biorxiv

Glycobiology Part 3 N Glycosylation Flashcards Quizlet

S Protein Glycosylation Pattern Revealed European Biotechnology

The Two Major Types Of Protein Glycosylation The Attachment Of Sugar Download Scientific Diagram

Click Reagents For Glycosylation Jena Bioscience
1

Structural Biochemistry Proteins Protein Glycosylation Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Glycoprotein Wikipedia

Genetic Diseases Associated With Protein Glycosylation Disorders In Mammals Intechopen

The Mechanism Of N Linked Protein Glycosylation The Core Oligosaccharide Is Assembled And Attached To Dolichol Pho Molecular Biology Biochemistry Cell Biology
Plos One Abnormal Protein Glycosylation And Activated Pi3k Akt Mtor Pathway Role In Bladder Cancer Prognosis And Targeted Therapeutics

Effect Of Glycosylation On Protein Folding A Close Look At Thermodynamic Stabilization Pnas
Protein Glycosylation And Its Associated Disorders



