Pcr Primers Diagram
Q Tbn 3aand9gcszzhknn2u9bn S5rby7j 6g4ugqs1tyactlxpbr Bg9idfwqhb Usqp Cau
Why We Need Antigen And Antibody Tests For Covid 19 The Native Antigen Company

Schematic Summary Of Arms Pcr Primer Design And Dna Gel Patterns Of The Download Scientific Diagram
Pcr The Basics Of The Polymerase Chain Reaction Medical Laboratory Observer

Setting Up The Pcr Reaction Nebnext Multiplex Oligos For Illumina Dual Index Primers Set 2 E7780 Neb

What Is Pcr Polymerase Chain Reaction Facts Yourgenome Org
A Basic Polymerase Chain Reaction Protocol.
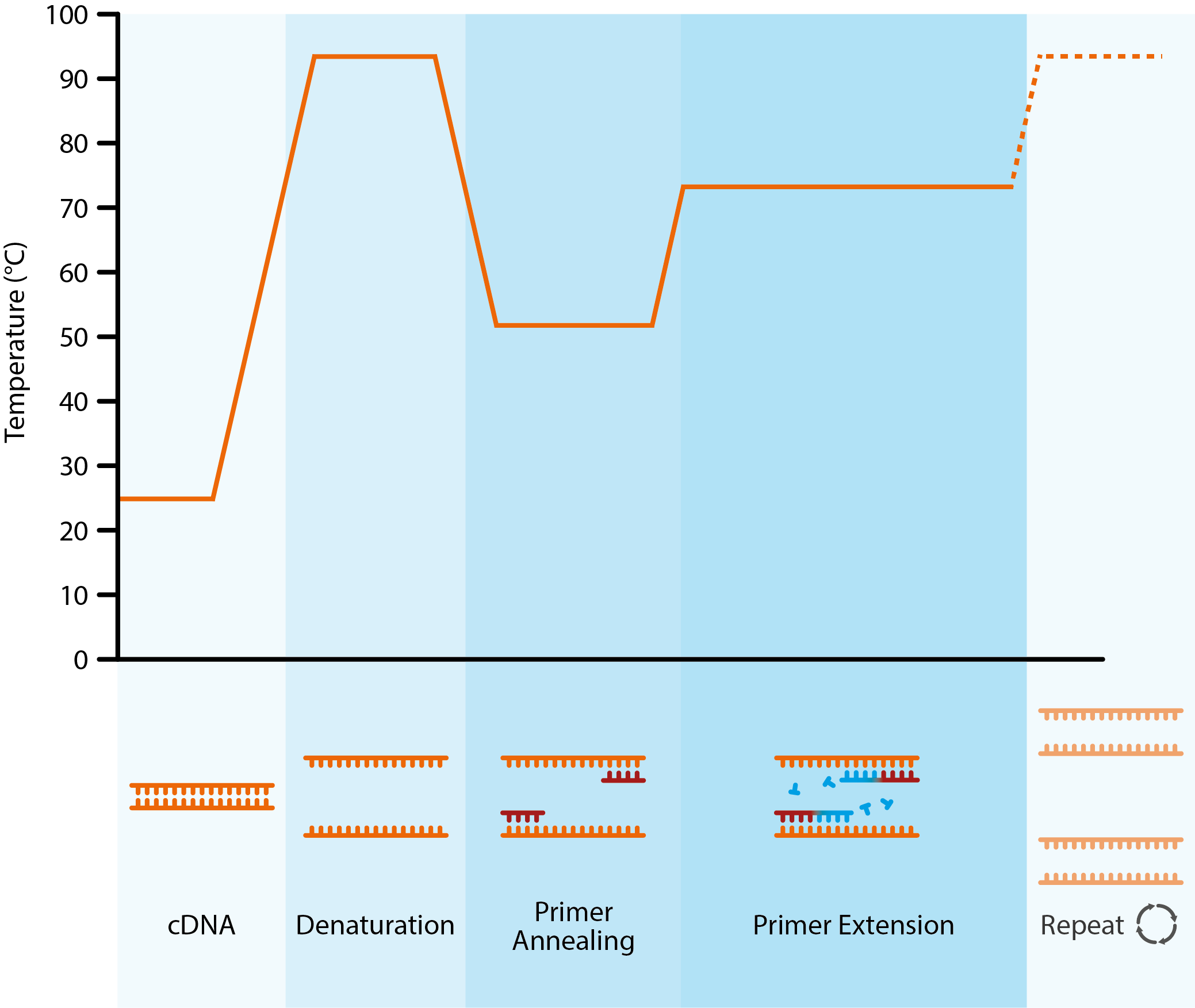
Pcr primers diagram. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) AP.BIO:. The amplification of a specific cDNA by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Ensure that a valid combination of i7 and i5 primers is used.
Making identical copies, in this context, is known as cloning.In the diagram below, the gene of interest (f) is inserted into a plasmid, creating recombinant DNA. How Polymerase Chain Reaction Works Gene copies are made using a sample of DNA, and the technology is good enough to make multiple copies from one single copy of the gene found in the sample. LUX PCR Primers These assays employ two DNA primers, one of which is a hairpin-shaped PCR primer with a fluorescent reporter attached near the 3' end, as illustrated in Figure 8.
Furthermore, two PCR primers;. Please refer to the diagram below. The polymerase enzyme can only add DNA bases to a double strand of DNA.
If the temperature is too low, the primer may bind imperfectly. (A) Diagram of the structure of the clone with gap and PCR primers designed shown. Hence, primers are served as starting points of the synthesis of new strands.
PCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction is a technique used in molecular biology to create several copies of a certain DNA segment. The PCR process was originally developed to amplify short segments of a longer DNA molecule (Saiki et al. Such synthetic nucleotides can be readily produced with automated instruments based on the standard reaction scheme.
In contrast, a machine designed to carry out PCR reactions can complete many rounds of replication, producing. It is a fast and inexpensive way to amplify, or make many copies of, small segments of DNA.This is necessary because methods used for analyzing DNA (determining the DNA base pair sequence) require more DNA than may be in a typical sample. The Polymerase Chain Reaction (With Diagram) Article Shared by.
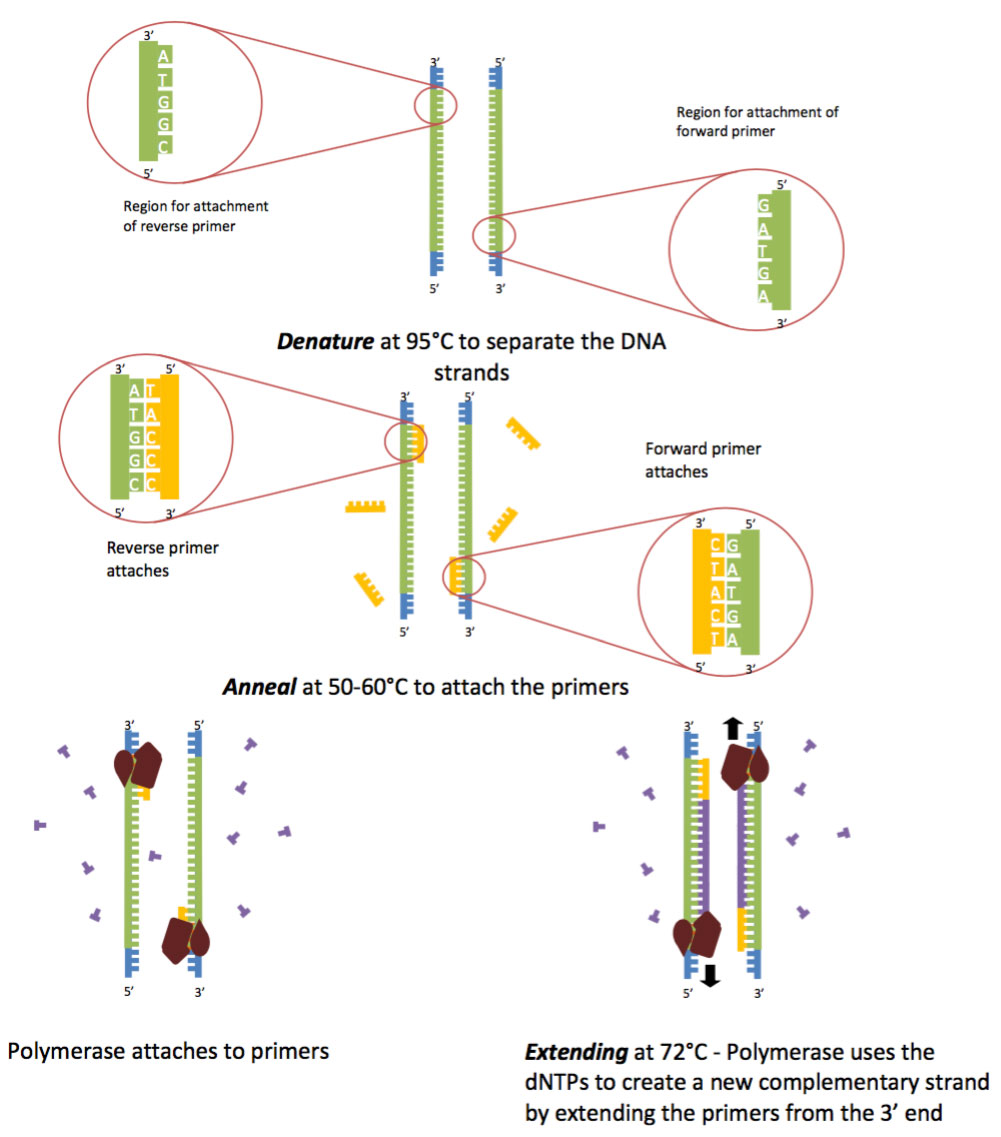
A typical PCR procedure begins by heat-denaturation of a DNA sample into single strands. At the annealing step, DNA primers line up on exposed nucleotide sequences at the DNA target according to base-pairing rules. Combining the index primers during the PCR amplification step.
IST‑1 (EU), IST‑1.P (LO), IST‑1.P.1 (EK) A technique used to amplify, or make many copies of, a specific target region of DNA. (B) PCR product covering the gap. Polymerase chain reaction steps.
This is a typical temperature-dependent DNA :. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the cardinal laboratory technology of molecular biology. It is a simple, cost-effective technique.;.
A primer dimer (PD) is a potential by-product in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common biotechnological method. Designing PCR Primers for Directional TOPO Cloning. The PCR mechanism is as simple as its purpose:.
Include all the steps, labeled and in the right order. PCR has been one of the most important techniques developed in recent years. LAMP is highly sensitive and specific DNA/RNA amplification technique.;.
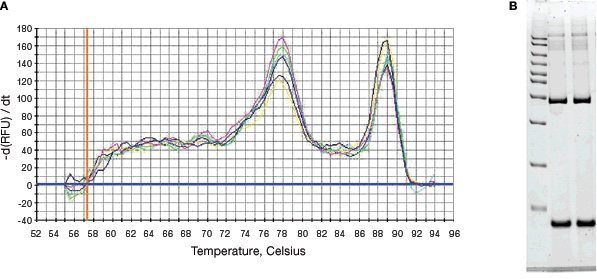
The reporter is quenched by the secondary structure of the hairpin. Although the melt profile suggests products of varying Tm, the gel image indicates that a single amplicon is present. Depending on the pET TOPO vector you are using, consider the following when designing your PCR primers.
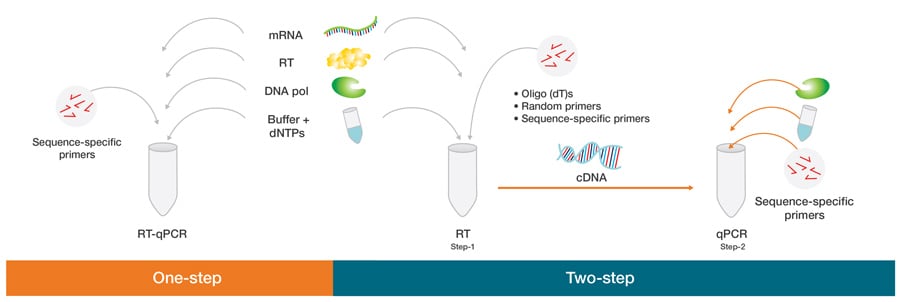
A) A melt profile and B) agarose gel analysis of a SYBR green I reaction. Thus, the term nested PCR. Oligo (dT) primers, random primers, and sequence-specific primers are three types of primers commonly used here.
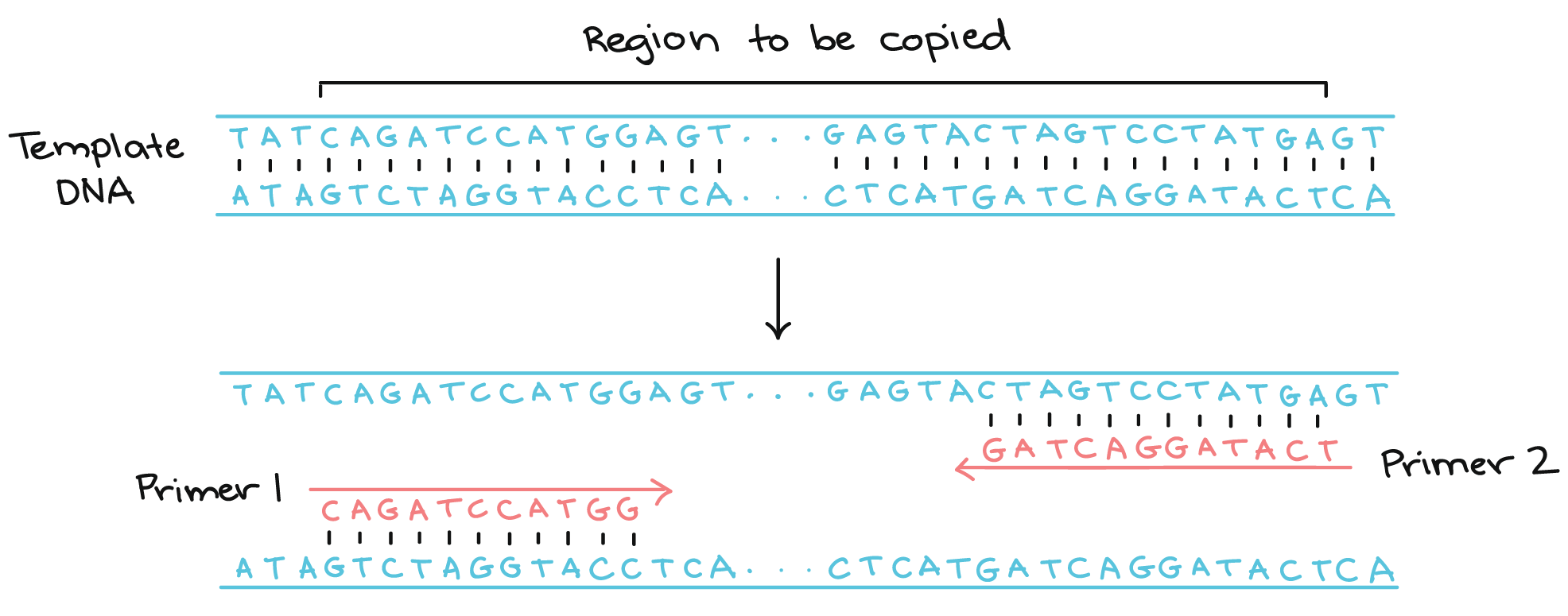
We can avoid most of these problems using primers of 15- nucleotides in length (note that the examples in the diagrams below use 5 nucleotide primers for simplicity – we would not use these in a real PCR. (If you are completing this handout online, draw the diagram on a piece of paper, take a photo, save the image as a PDF, and upload it in the space below.) 2.What does the Master Mix contain?. The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique for the amplification of DNA in vitro (this describes experiments with cells outside their normal environment).
Lastly, the forward and reverse primers should not be complementary, or they will anneal to each other and form a “primer dimer”. Used to see if PCR can produce the desired product Internal amplification control (not included in all PCR):. The set of primers should flank the fragment you intend to amplify from the DNA template.
The primers are designed to be complementary in sequence to short sections of DNA on each end of the sequence to be copied. CHAPTER 1 i7 primers PCR plate i5 primers 1.1A.1. End of the First PGR Cycle.
Nested PCR – Once the initial PCR cycle is done, another PCR is done but this time with the use of a new primer nested within the original primer. The 1 st PCR aims to connect the target ORF sequence with the 2 nd forward/reverse primers (please see the diagram below). Nested PCR reduces the nonspecific amplification of the target sequence.
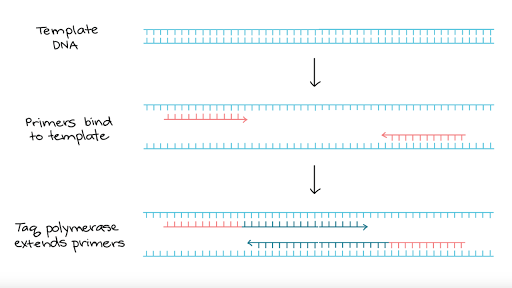
Since DNA is double stranded, two types of primers are needed in PCR. Second polymerase chain reaction step – DNA Primer annealing. Control samples known to contain desired DNA;.
In vivo, the enzyme, DNA polymerase requires a primer for the initiation of DNA replication. PCR was developed in 19 by Kary B. To sensitive and prone to contamination and small changes in condition Applications Complicated primer design vDisadvantages.
PCR enables the production or amplification of billions of copies of an original piece of DNA in the tube with minutes or hours. The below given article will help you to understand the following things:- 1. PCR is important because it can generate several copies of a DNA sequence in a very short time.
RT-PCR (Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction) is a highly sensitive technique for the detection and quantitation of mRNA (messenger RNA). This length is long enough for adequate specificity and short enough for primers to bind easily to. A typical annealing temperature is about 3-5 °C below the Tm of the primers used.
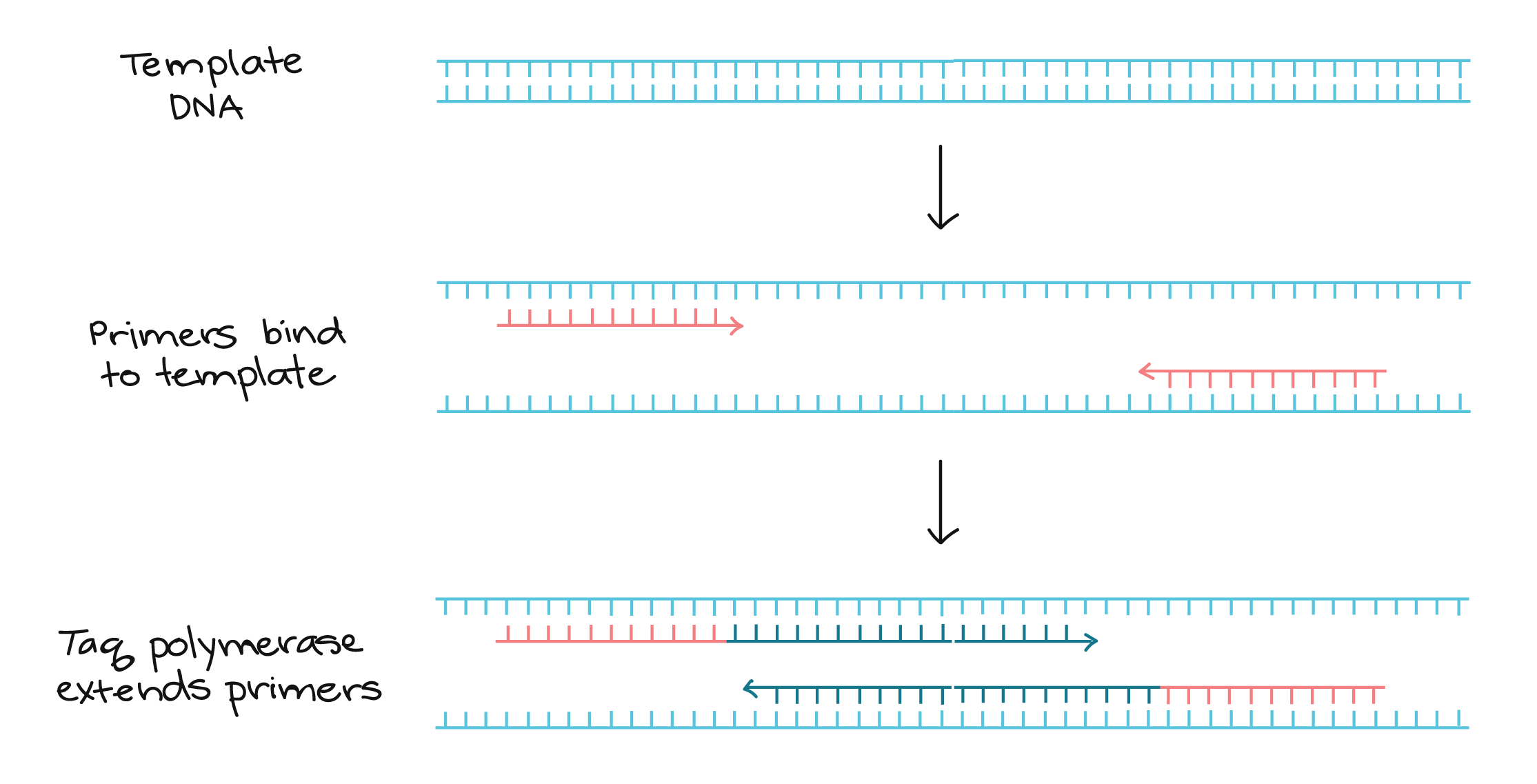
1) double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) is heat denatured, 2) primers align to the single DNA strands and 3) the primers are extended by DNA polymerase, resulting in two. The reason for doing so is to reduce the risk of unwanted products. Real PCR primers are longer, often from to 40 nucleotides long.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it to a large enough amount to study in detail. They are known as forward primer and reverse primer. Notice that the primers are complementary to the flanking sides of the DNA sequence of interest.
On the polymerase chain reaction page, I showed a simple diagram of how PCR works. To detect HIV, PCR primers are made for sequences in the virus, and a. The forward primer will anneal with 3’-5’ DNA strand and the reverse primer will anneal with the 5´-3’ DNA strand.
Scorpions PCR primers contain a sequence complementary to an internal portion of the target sequence. Taq polymerase works only in 5’ to 3’ direction hence the DNA synthesis occurs in the same 5’ to 3’ direction. Before the development of PCR, the methods used to amplify, or generate copies of, recombinant DNA fragments were time-consuming and labour-intensive.
Primers are single strands of DNA or RNA sequence that are around to 30 bases in length. Assembly PCR – Overlapping primers are used to amplify longer fragments of DNA. This design reduces the risk of false positives from amplification of any contaminating genomic DNA, since the intron-containing genomic DNA.
Genscript online pcr primer design tool for perfect PCR and sequencing primers design. The design of the PCR primers to amplify your gene of interest is critical for expression. PCR primers for the qPCR step of RT-qPCR should ideally be designed to span an exon-exon junction, with one of the amplification primers potentially spanning the actual exon-intron boundary (Figure 4).
The technique consists of two parts:. PCR stands for Polymerase Chain reaction. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Introduction PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a revolutionary method developed by Kary Mullis in the 1980s.
The second requirement for PCR is the ability to synthesize oligonucleotides at least 18– nucleotides long with a defined sequence. Primer design is a critical step in a PCR protocol. Mullis, an American biochemist who won the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1993 for his invention.
This tool is commonly used in the molecular biology and biotechnology labs. See Appendix A to verify that correct primer combinations have. There are two sets of forward and reverse primer sets.
In a previous tutorial, we explored how plasmids (letter “c” below) can be used to copy a gene. The polymerase chain reaction is a molecular genetic technique for making multiple copies of a gene and is also part of the gene sequencing process. We have applied thermodynamic and bioinformatic knowledge towards a suite of easy-to-use, online tools to help you design primers.
Annealing temperature for the PCR. Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Nested PCRs are sometimes necessary to compensate for inefficient first-round PCR due to primer mismatches so, if we can use well-matched primers for first-round PCR nested approach may not be needed in many circumstances. (C) Sequence analysis of the PCR product showing AT richness.
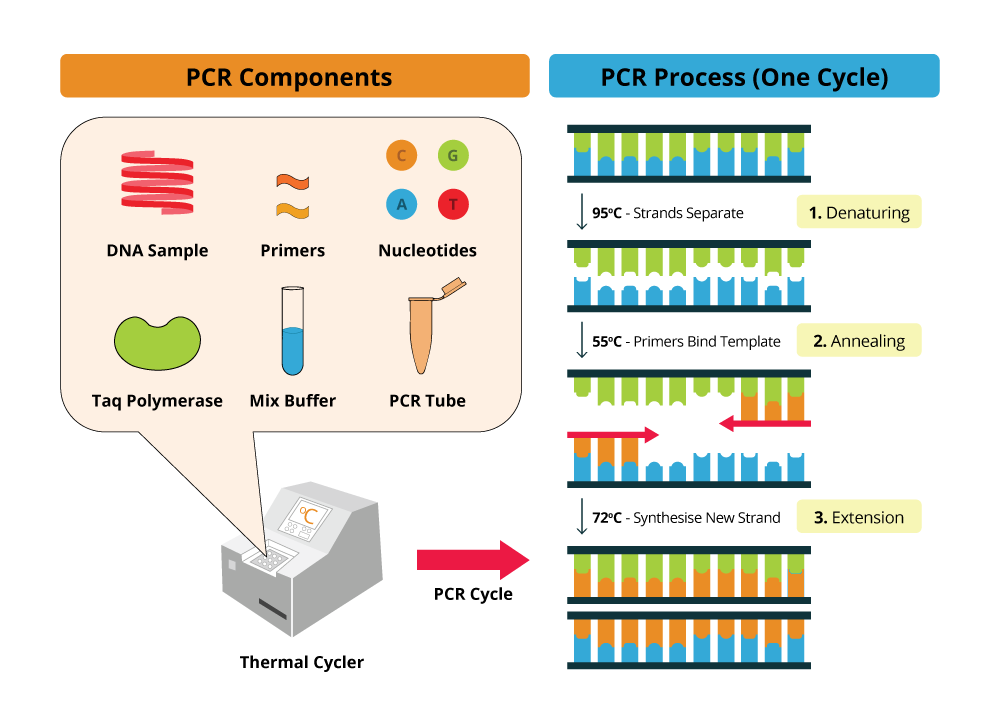
The diagram on the right illustrates the entire PCR process. This new technology, called Snake, was shown to supersede the conventional methods like TaqMan, Molecular Beacons, and Scorpions in the signal. The first step for a single cycle is the denaturation step, in which the double-stranded DNA template molecule is made single-stranded.
The temperature for this step is typically in the range of 95-100°C, near boiling. PCR is based on using the ability of DNA polymerase to synthesize new strand of DNA complementary to the offered template strand. Why is a primer added?.
Primers serve as the starting point for DNA synthesis. Real DNA sequences are more complex;. Following the WASP principles, two pairs of forward (or reverse) primers and a common reverse (or forward) primer were designed for TPMT*3B and TPMT*3C genotyping.
In that diagram, the nucleotides of the DNA are represented by a zippered line. The main difference between PCR primers and sequencing primers is that the PCR primers are important for PCR amplification to obtain an amplicon, whereas the sequencing primers are important for sequencing a DNA fragment to reveal its nucleotide sequence. However, which primer is applied, it depends on the type of RT-PCR assay.
Alternatively, 96-well deep well plates can be used and aligned against a PCR plate as in the diagram below. The function of reverse transcriptase plays an important role to make the present technique successful. It is generally accepted that the optimal length of PCR primers is 18-22 bp.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a test tube version of the same process of DNA replication that is found in the living cell. The synthesis of cDNA (complementary DNA) from RNA by reverse transcription (RT) and ;. Therefore, the 1 st PCR forward/reverse primers need to be target gene specific that overlap with the N-terminal and C-terminal sequences of the ORF of the target gene.
Introduction to genetic engineering. In fact, a repetitive sequence like GGGGG would be difficult to copy correctly. The polymerase chain reaction (PGR) amplifies a single piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, see figure 6.2.
The reason behind is its simplicity of the reaction and relative case of the practical manipulation steps. Gene Cloning Before PCR. 1.Summarize the process of PCR in a diagram.
Annealing Primer to Target Sequence 3. As a result, the DNA polymerase amplifies the PD, leading to competition for PCR reagents, thus potentially inhibiting. Let us make an in-depth study of the polymerase chain reaction, which is a technique for amplifying DNA sequences.
This allows for the Taq polymerase to synthesize the complementary strand, resulting in exponential duplication of the original DNA segment. As its name implies, a PD consists of two primer molecules that have attached to each other because of strings of complementary bases in the primers. PCR products were sequenced directly or cloned into pCR 2.1 with the Invitrogen TA Cloning Kit (Invitrogen, San Diego, Cal-if.) and then sequenced.
A schematic diagram illustrating the protocol for CRAS-PCR is presented in our previous study. Poor design choices, erroneous or truncated sequences, and ineffective purification can lead to unusable results. Contains a second set of primers and an unrelated target, which helps distinguish between a true neg and an amplification failure.
What is the importance of PCR?. Arguably one of the most powerful laboratory techniques ever discovered, PCR combines the unique attributes of being very sensitive and specific with a great degree of flexibility. Read this article to learn about the stages, primer design, types, sensitivity, factors affecting, applications and variations of polymerase chain reaction.
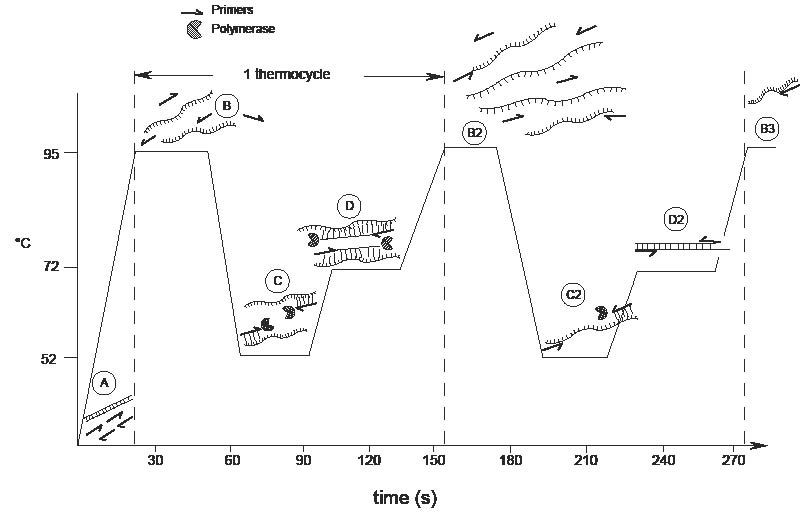
In general, a single PCR run will undergo 25-35 cycles. The addition of relatively short flap sequence at the 5′-end of one of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers considerably improves performance of real-time assays based on 5′-nuclease activity. The accuracy of design and synthesis of a primer pair is the most important consideration to generate good PCR performance data.
The PCR is …. A single PCR reaction involves three temperature-dependent steps, described as follow:. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
Primers are an essential component in the amplification of DNA both in vivo and in vitro. A typical amplification reaction includes target DNA, a thermostable DNA polymerase, two oligonucleotide primers, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), reaction buffer and magnesium. Because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a preexisting 3'-OH group, it needs a primer to which it can add the.
For standard PCR, all you need is a DNA polymerase, magnesium, nucleotides, primers, the DNA template to be amplified and a thermocycler. Denaturation by Heat 2. LAMP is an innovative molecular diagnostic field and can be used for the diagnosis of infectious diseases, food inspection, environmental.
The forward and reverse primer are used in a PCR while sequencing requires a single sequencing primer. Stable hydrogen bonds between complementary bases are formed only when the primer sequence very closely matches the template sequence. If it is too high, the primer may not bind at all.
DNA hybridization reaction and has to be optimized. The amplification of gene is done by using the technique of PCR. Some of the major steps involved in polymerase chain reaction in DNA sequence are:.
In vitro, primers are mostly used for the initiation of polymerase chain reaction (PCR).Some other techniques including sequencing, cloning, site-directed mutagenesis, etc. PCR was invented in 1984 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation.It is fundamental to much of genetic testing including analysis of.

Pcr
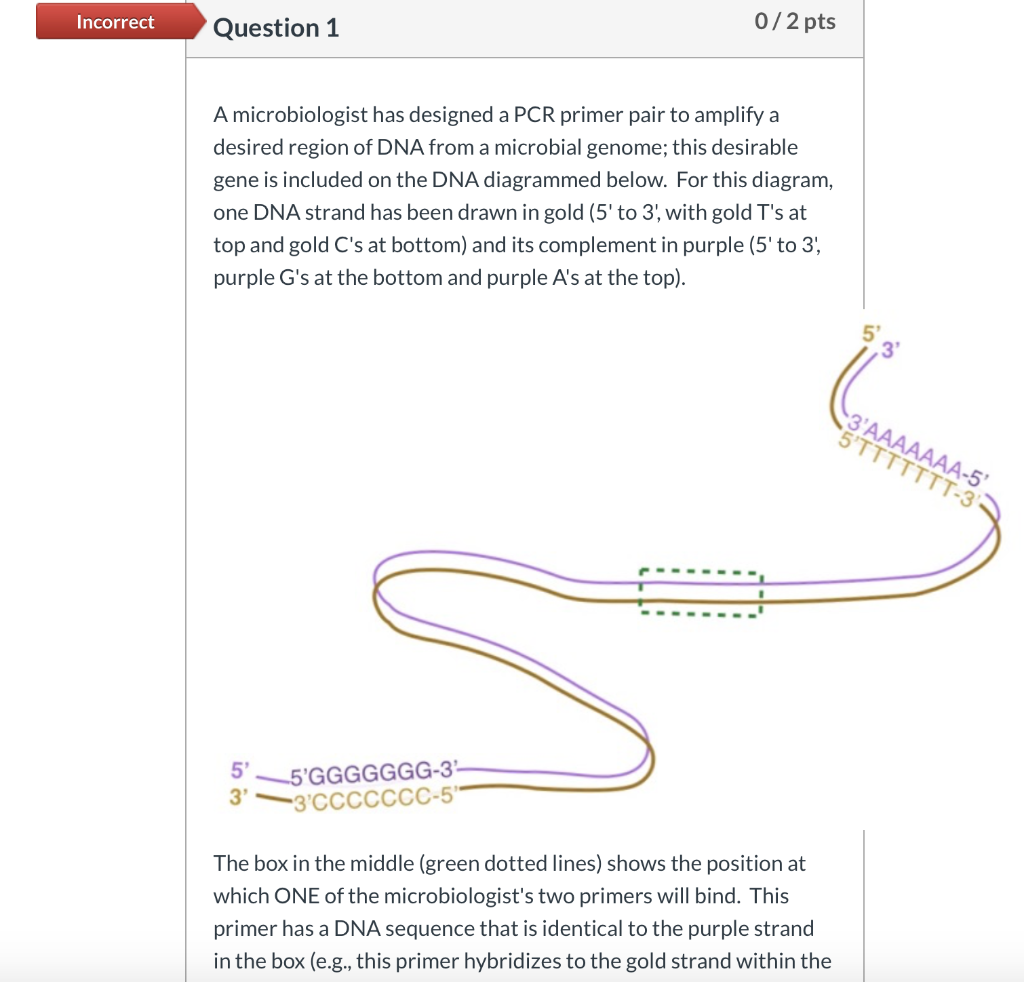
Solved Incorrect Question 1 0 2 Pts A Microbiologist Has Chegg Com
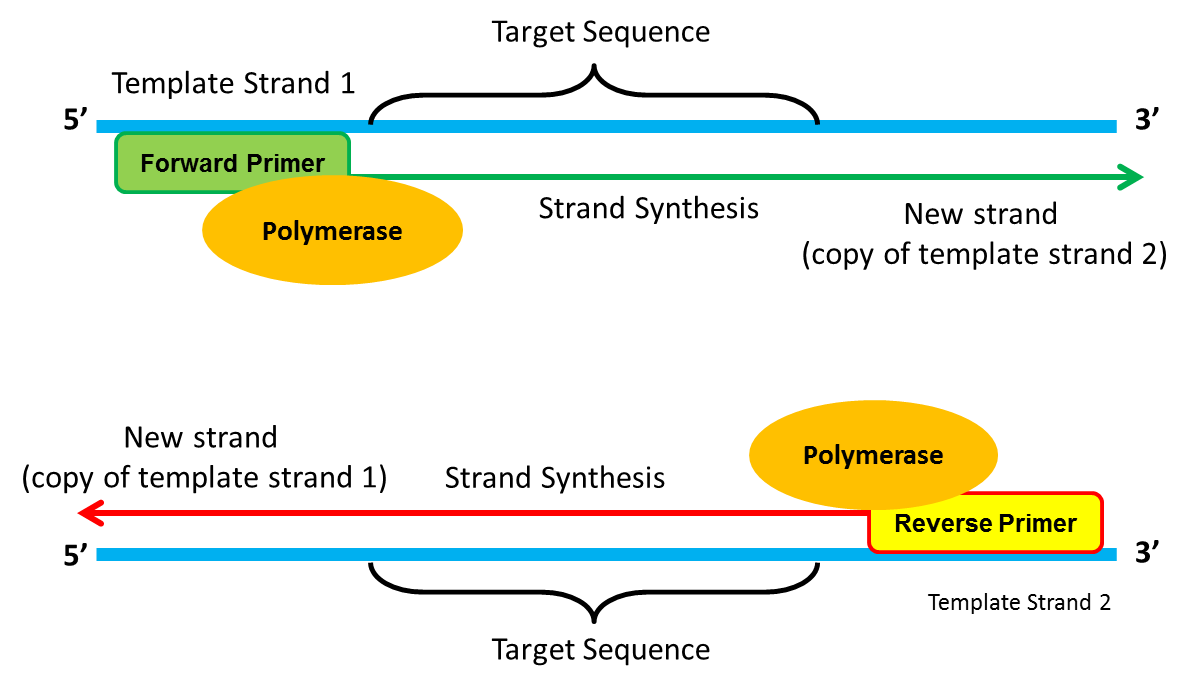
A Cornerstone Of Molecular Biology The Pcr Reaction Antisense Science
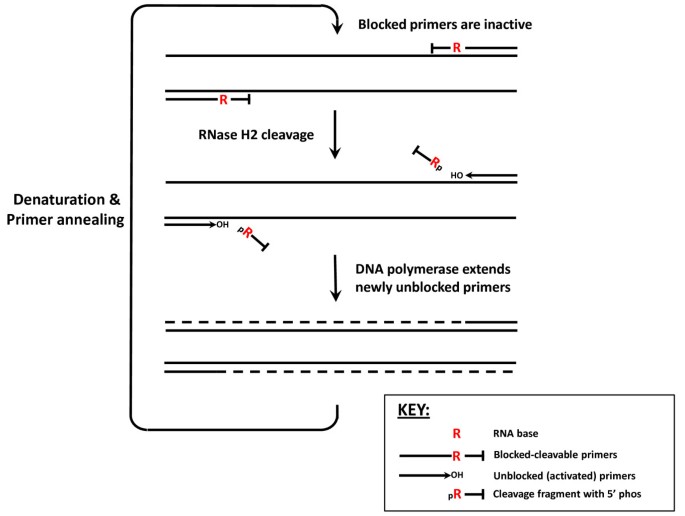
Rnase H Dependent Pcr Rhpcr Improved Specificity And Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Detection Using Blocked Cleavable Primers Bmc Biotechnology Full Text
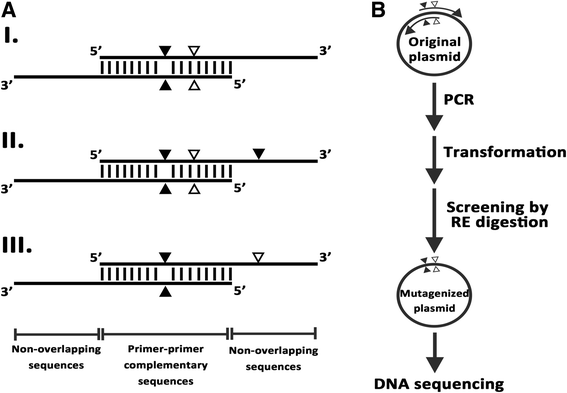
Enhanced Mutant Screening In One Step Pcr Based Multiple Site Directed Plasmid Mutagenesis By Introduction Of Silent Restriction Sites For Structural And Functional Study Of Proteins Springerlink
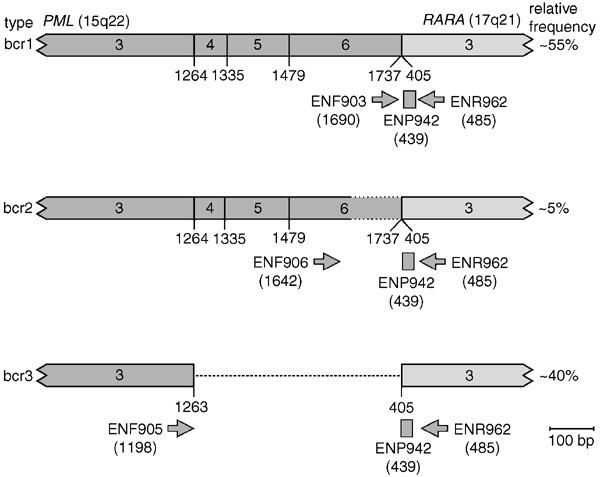
Standardization And Quality Control Studies Of Real Time Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction Of Fusion Gene Transcripts For Residual Disease Detection In Leukemia A Europe Against Cancer Program Leukemia

Pcr Primers Eurofins Bioz Ratings For Life Science Research
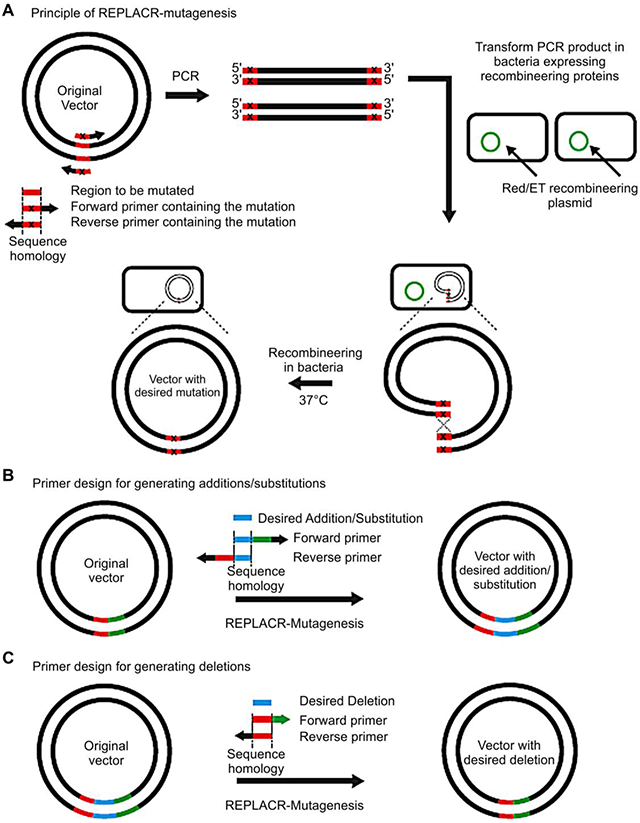
Site Directed Mutagenesis By Polymerase Chain Reaction Intechopen
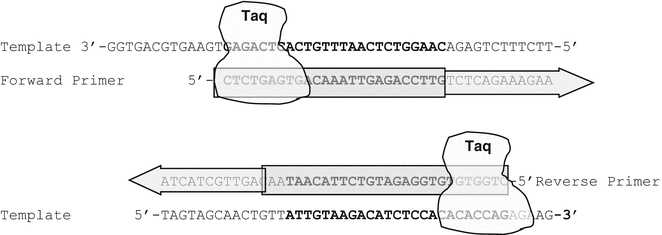
Primer Design For Pcr Reactions In Forensic Biology Springerlink
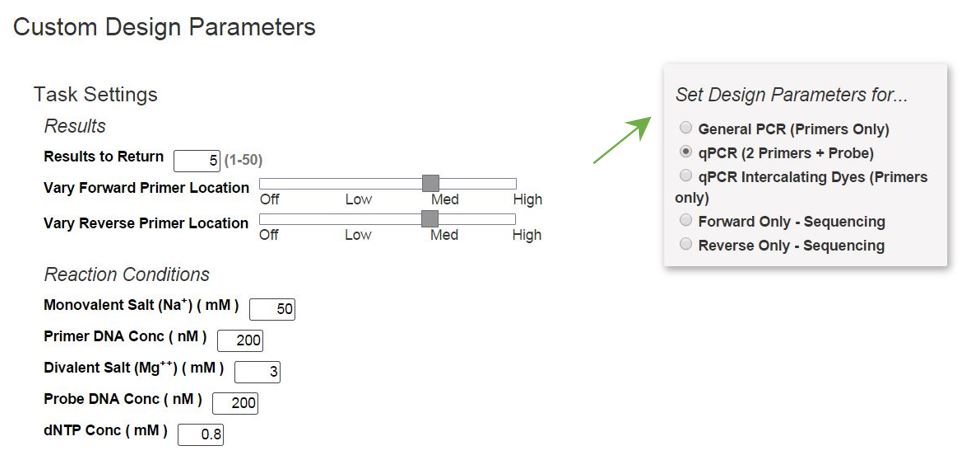
Using Primer Design Tools For Pcr Qpcr Idt

Dna Primer An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Mlab 2378 Fundamentals Of Molecular Diagnostics Links

Sequencing Forensic Analysis And Genetic Analysis

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Molecular Biology The Biology Notes

Overhang Pcr

Real Time Pcr Qpcr Technology Basics Biosistemika

Solved 2 You Are A Scientist Studying The Gene Raf1 Whic Chegg Com
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=601&height=479)
6 5 Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Biology Libretexts

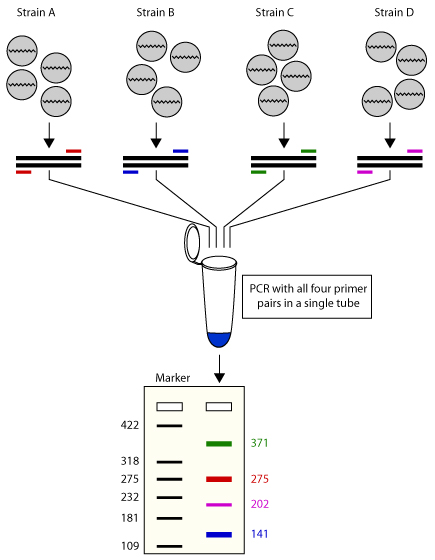
Multiplex Pcr An Overview Of Multiplex Pcr Assay Primer Design For Multiplexing Primer Design Software For Multiplex Pcr

How Is The Amplification Of Gene Done Using The Technique Of Pcr Explain With The Help Of Diagram
%20PCR%20works_big.png)
Rt Pcr Reverse Transcription Pcr Sigma Aldrich

Linear After The Exponential Late Pcr An Advanced Method Of Asymmetric Pcr And Its Uses In Quantitative Real Time Analysis Pnas

Schematic Diagram Of Nested Pcr The First Pair Of Primers Amplifies Download Scientific Diagram

Crosslinking Of Pcr Primers Reduces Unspecific Amplification Products In Multiplex Pcr Sciencedirect
Pcr And Molecular Biology Fundamental Principles
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs4odcmvxrqmgg1rkwiwzzmacyljwtbifdjap Tatc1xg7l Nli Usqp Cau
With The Sequences For Sites A And B As Mapped On Chegg Com

Schematic Drawing Of The Prase Procedures A Nested Mul Open I
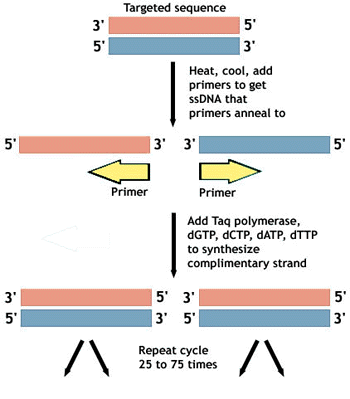
The Different Phases Of Pcr And Why They Are Important
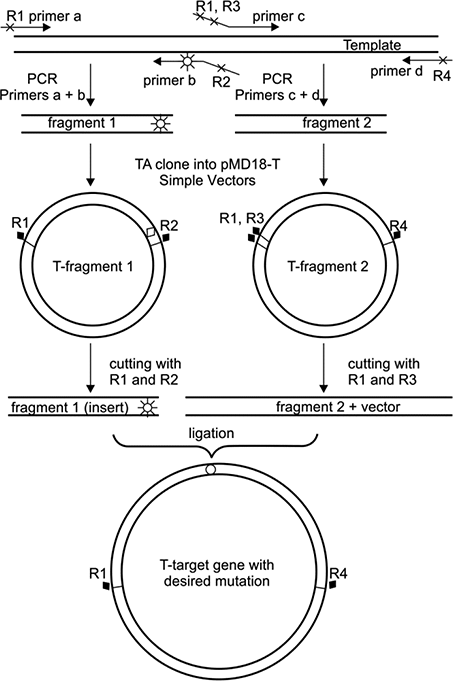
Site Directed Mutagenesis By Polymerase Chain Reaction Intechopen
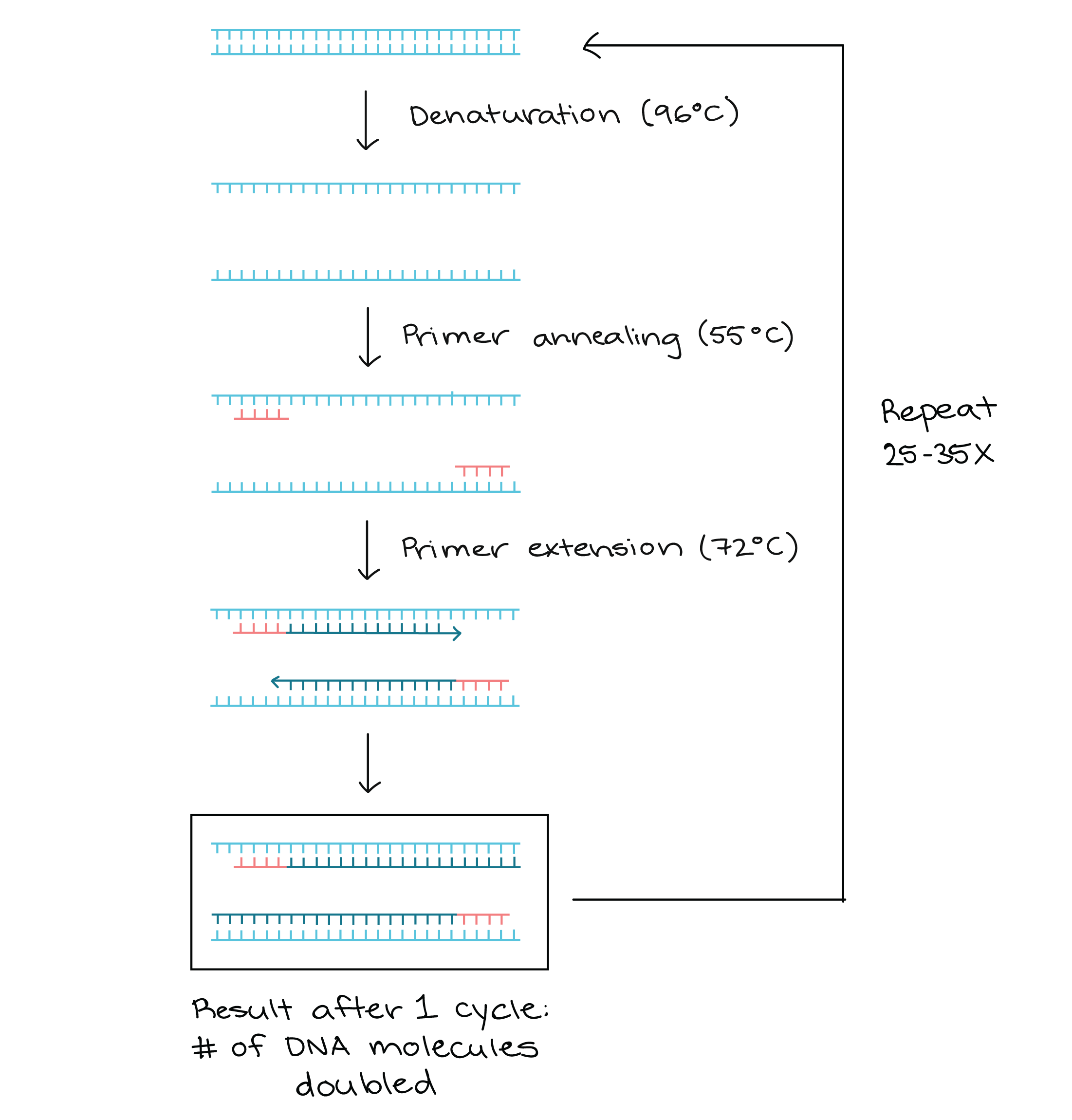
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Article Khan Academy

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Article Khan Academy
Http Www Aun Edu Eg Molecular Biology Workshop realtime 17 2 realtime pcr final Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqzninymvxcoxl6ityd4zga 5jbhu67honfuwvj3pcas6qidmae Usqp Cau

Polymerase Chain Reaction Wikipedia

Multiplex Pcr Primer Design Software Panelplex Information Dissemination Media For Research And Development Tegakari

Colony Pcr Exercises Pathways Over Time

Real Time Pcr Principle Procedure Advantage Limitations And Applications

Diagram Of The Dual Primer Labeling And Multiplexing Method In The Fi Download Scientific Diagram

If We Add Only 1 Primer In Pcr Biology Stack Exchange
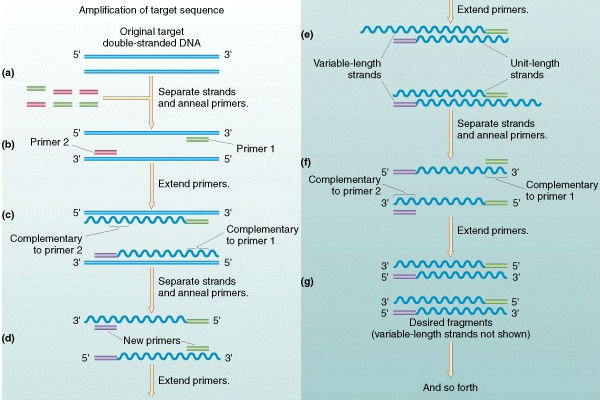
Pcr In Detail

Pcr Protocol Pcr Steps How To Do Pcr
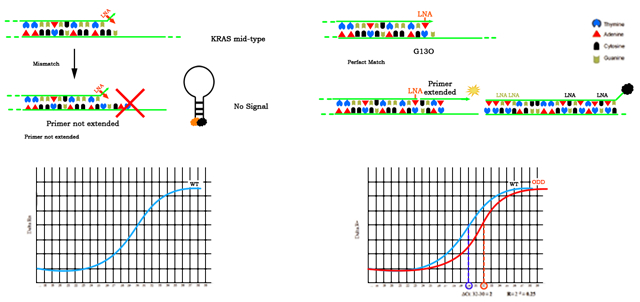
Allele Specific Bna Primer Design

Custom Dna Sequencing Sequencing Optional Services Hokkaido System Science Co Ltd

Gene Quantification Real Time Pcr Dyes And Chemistries

Rt Qpcr Quantitative Reverse Transcription Pcr Sigma Aldrich
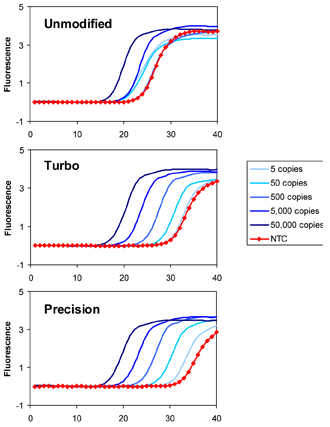
Glen Report 21 11 Hot Start Pcr Update Cleanamp Primers

Schematic Depiction Of Gap Primer Pcr Gppcr Based Formation Of Dna Download Scientific Diagram

Reverse Transcriptase Cdna Overview Applications Goldbio

Pcr For Sanger Sequencing Thermo Fisher Scientific Us
Biorender Life Science Icons

Pcr Introduction Abm Inc

Schematic Outline Of Inverse Fusion Pcr Cloning Ifpc Primer Design
Diagram Indicating Pcr Primer Positions And Amplicon Sizes Primers Hs1 Download Scientific Diagram
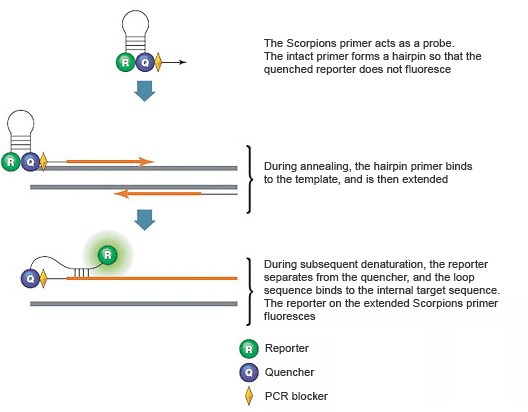
Introduction To Pcr Primer Probe Chemistries Lsr Bio Rad
Qpcr Assay Design And Optimization Lsr Bio Rad

Pcr Primer Desining

Pcr
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Diamantina Institute University Of Queensland
Basic Principles Of Rt Qpcr Thermo Fisher Scientific Us
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Article Khan Academy

Pcr Primers A Primer Virology Down Under

Pcr Reaction Ten Secrets That Nobody Tells You Plant Science Primer Design Dna Polymerase

Pcr And Directed Mutagenesis
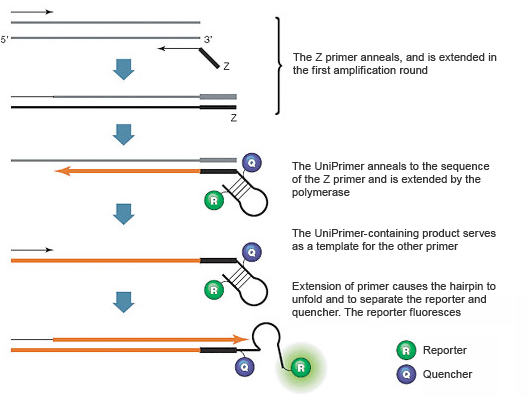
Introduction To Pcr Primer Probe Chemistries Lsr Bio Rad
Imatinib Independent Aberrant Methylation Of Nov Ccn3 In Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients A Mechanism Upstream Of r Abl1 Function Cell Communication And Signaling Full Text

Fd 5357 Diagram Showing Steps Of Pcr Download Diagram
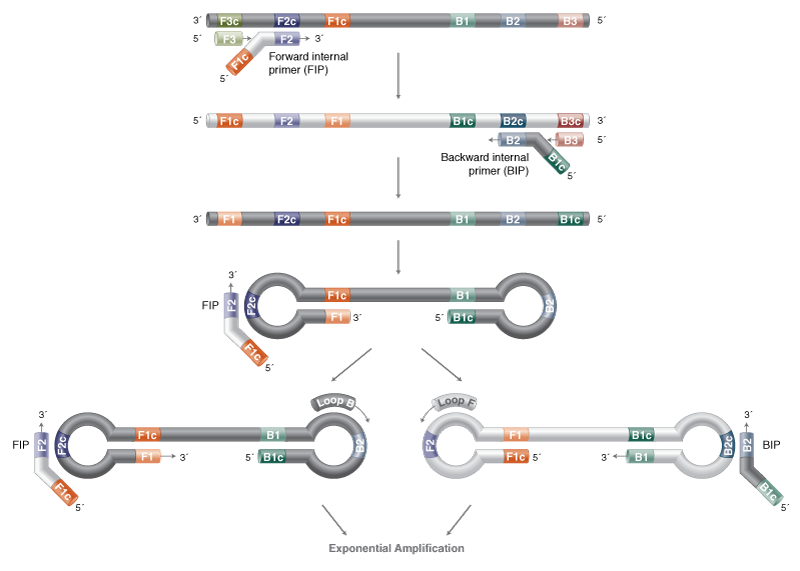
Isothermal Amplification Strand Displacement Neb
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqykfx 4rc901zg0gssn58qeemi Jy44szssmj X91mtptrbgdk Usqp Cau
Plos One Novel Pcr Primers For The Archaeal Phylum Thaumarchaeota Designed Based On The Comparative Analysis Of 16s Rrna Gene Sequences
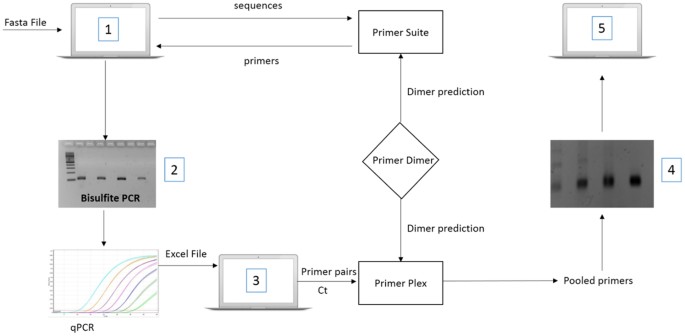
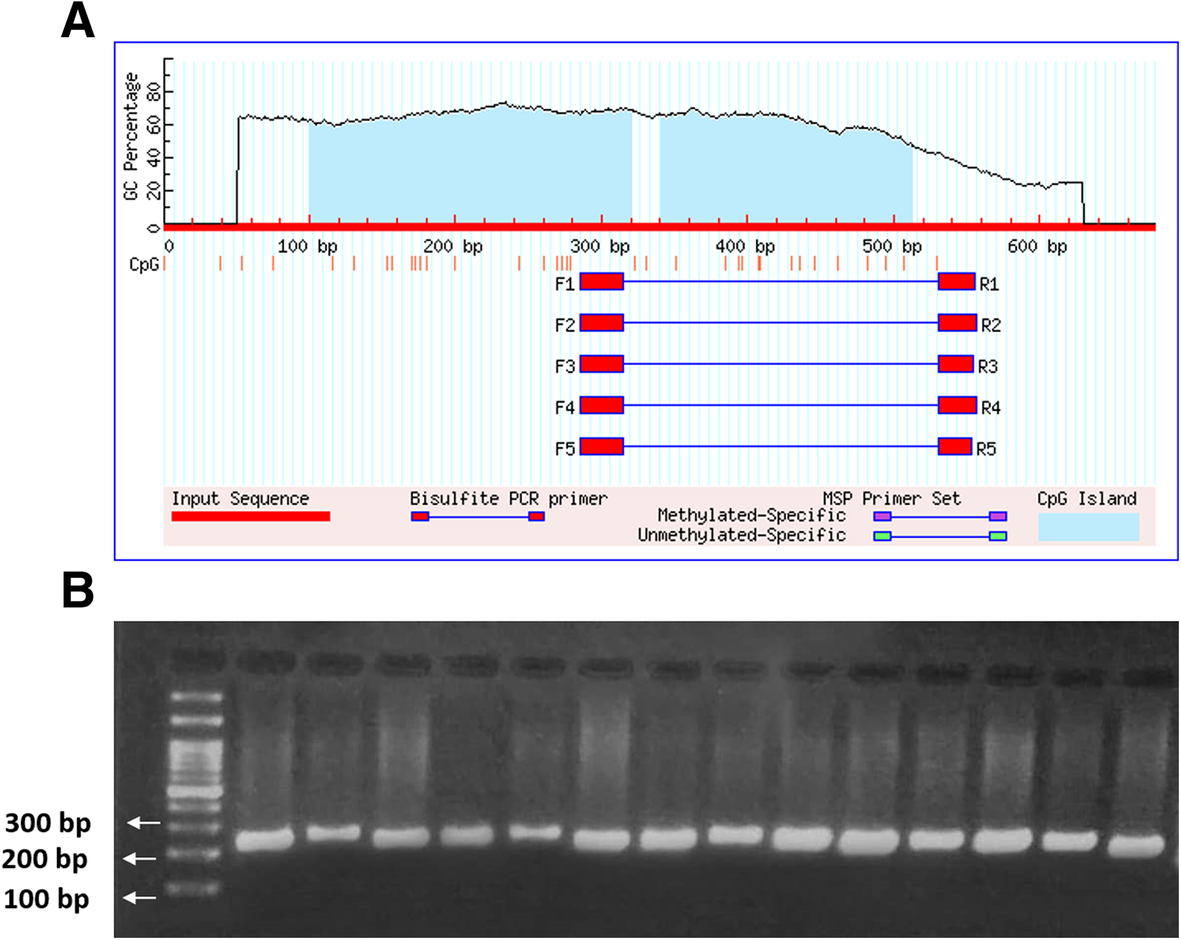
Primersuite A High Throughput Web Based Primer Design Program For Multiplex Bisulfite Pcr Scientific Reports

Expanded Genetic Alphabets In The Polymerase Chain Reaction Yang 10 Angewandte Chemie Wiley Online Library

Addgene Plasmid Cloning By Pcr With Protocols
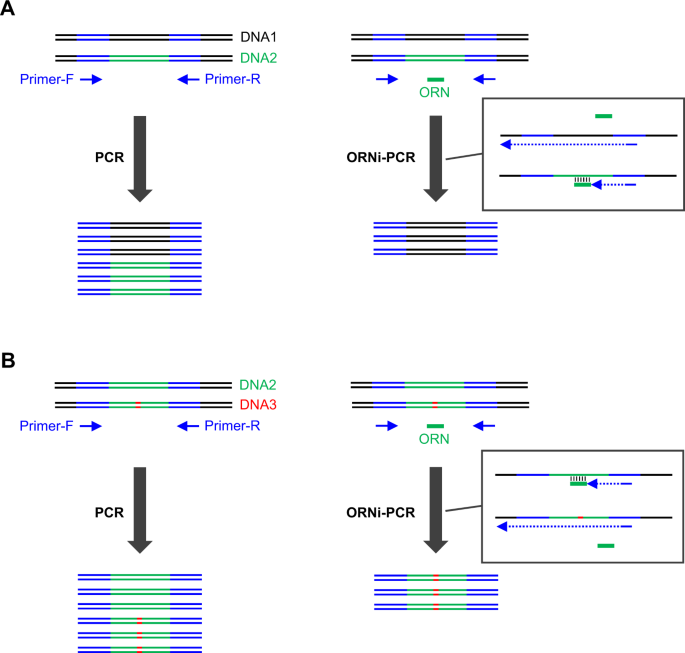
A Refined Two Step Oligoribonucleotide Interference Pcr Method For Precise Discrimination Of Nucleotide Differences Scientific Reports
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Article Khan Academy

Pcr Primer Design Guidelines

Diagram Of Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Primer Design A Download Scientific Diagram

Addgene Protocol How To Design Primers
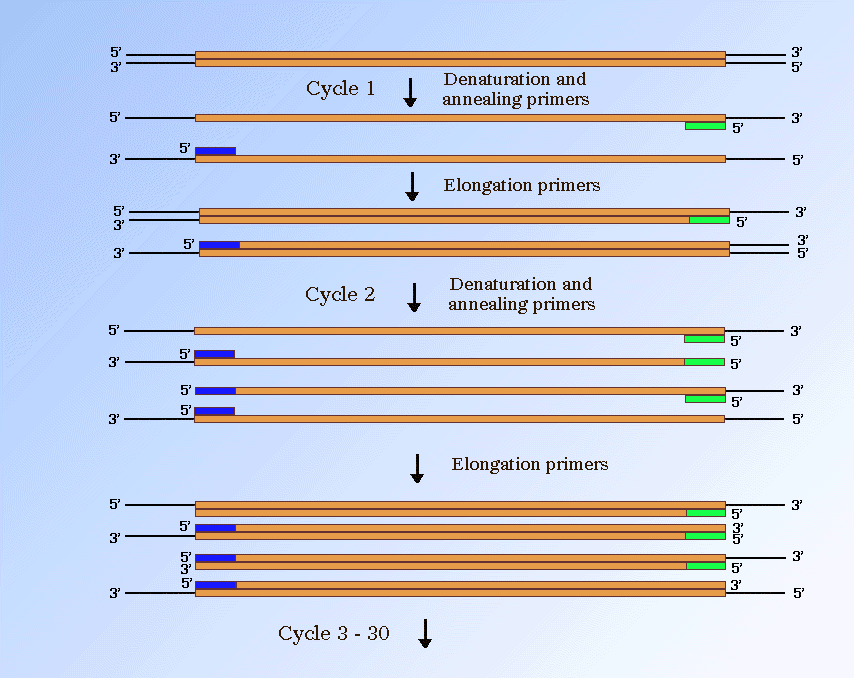
Diagram Of Pcr

Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Microrna Gene Primer Diagram Genotyping Transparent Png

Sequencing Forensic Analysis And Genetic Analysis
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Article Khan Academy

Gene Quantification Real Time Pcr Dyes And Chemistries

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Diamantina Institute University Of Queensland

ged Highly Degenerate Primer Thdp Pcr For Community

Pcr Overview Goldbio

Specific And Effective Detection Of Anammox Bacteria Using Pcr Primers Targeting The 16s Rrna Gene And Functional Genes Sci Total Environ X Mol

The Most Common Questions About Our Indexing Pcr And Sequencing Primer Kit
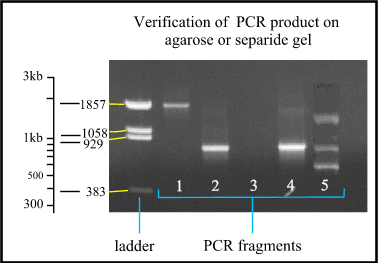
Principle Of The Pcr

Barcode Of Life Simple Laboratory Workflows For 16s And Co1 Genus And Species Identification

Figure 1 From Use Of Pcr Primers Containing A 3 Terminal Ribose Residue To Prevent Cross Contamination Of Amplified Sequences Semantic Scholar

Site Directed Mutagenesis By Polymerase Chain Reaction Intechopen
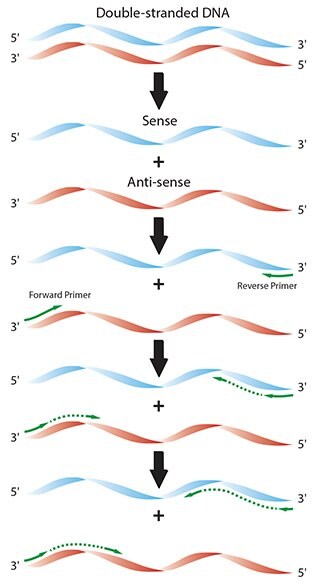
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Process Guide Sigma Aldrich
Real Time Pcr Quantification Of Spliced X Box Binding Protein 1 Xbp1 Using A Universal Primer Method

What Is Pcr Science Learning Hub

How To Calculate Pcr Primer Efficiencies
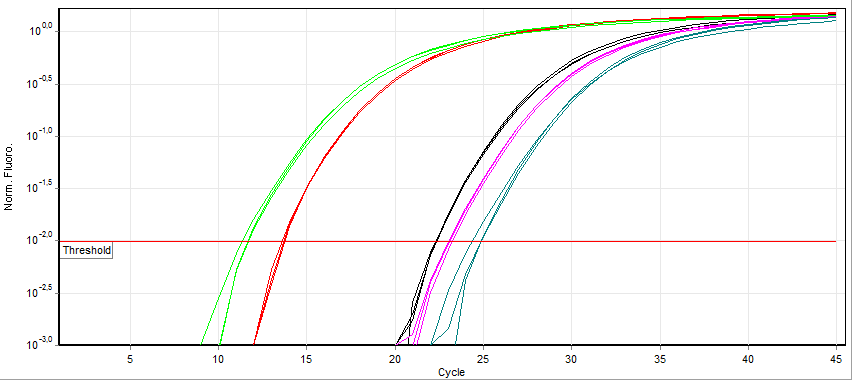
Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Wikipedia

Improved Pcr Specificity With Hot Start Pcr Primers Biotechniques



