Pcr Primer Annealing

Polymerase Chain Reaction Wikipedia
Biorender Life Science Icons
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Process Guide Sigma Aldrich

Pcr Overview Goldbio
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=601&height=479)
6 5 Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Biology Libretexts

Hot Start Pcr Wikipedia
Annealing temperature – The annealing temperature of the experiment should be 5 °C below the melting temperature of each primer.

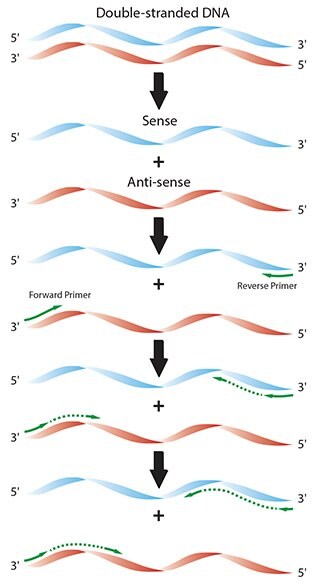
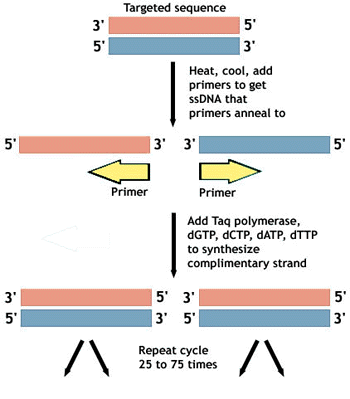
Pcr primer annealing. In the second PCR step, primers bind to complimentary DNA template sequences. During a typical PCR, cycles of denaturation, annealing and extension are repeated to achieve exponential amplification of the target sequence. PCR involves a series of temperature cycles.
Recalculate primer Tm values using the NEB Tm calculator;. PCR is based on using the ability of DNA polymerase to synthesize new strand of DNA complementary to the offered template strand. For ideal amplification, the best primers are 17 to 24 bases long.
Annealing Time An annealing time of 30-45 seconds is commonly used in PCR reactions. When using Thermo Scientific Phusion or Phire DNA polymerases or master mixes, we recommend calculating primer annealing temperatures using a T m calculator, which is based on the modified Breslauer's method 1.The tables below describe how to use the calculator and a few notes about primer design. At the annealing step, DNA primers line up on exposed nucleotide sequences at the DNA target according to base-pairing rules.
However, this use of a lower temperature permits a small amount of mismatching between primers and template, which may allow primers to bind to incorrect sites and gen. T a Opt = 0.3 x (T m of primer) + 0.7 x (T m of product) – 14.9;. Annealing to both exons is necessary as this ensures annealing to the exon-exon junction region but not either exon alone.
Polymerase chain reaction steps. Typically, use a 10–30 second annealing step at 3°C above the T m of the lower T m primer. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Introduction PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a revolutionary method developed by Kary Mullis in the 1980s.
65C you can use a 2 step PCR in which after an initial denaturation cycle the annealing and extension. The temperature is increased to 72 °C, which is optimum for DNA polymerase activity to allow the hybridized primers to be extended. Second polymerase chain reaction step – DNA Primer annealing.
Polymerase Chain Reaction Disadvantages Optimizations required Annealing temperature Number of cycles Small order of magnitude sensitivity for detection Real time PCR Similarities to regular PCR Same use of primers, template, enzyme, and nucleotides Differences from regular PCR Special machine Optical dyes Optimizations. Verify that primers are non-complementary, both internally and to each other. A variant of PCR that aims to reduce nonspecific background by gradually lowering the annealing temperature as PCR cycling progresses.
I used KOD polimerase and two different PCR programs, both similar to those Mr Stuart proposed, with the annealing temperature for M13 primers of 50ºC and 55ºC. Increase in annealing time up o 2-3 minutes did not appreciably influence the outcome of the PCR reactions. LUX PCR Primers These assays employ two DNA primers, one of which is a hairpin-shaped PCR primer with a fluorescent reporter attached near the 3' end, as illustrated in Figure 8.
Denaturation, primer annealing, and primer extension. The calculator calculates recommended T m (melting temperature) of primers and PCR annealing temperature based on the primer pair sequence, primer concentration, and DNA polymerase used in PCR. If this construct is stable enough, the DNA polymerase will bind and extend the primers according to the complementary sequence (step II in the figure).
Optimizing the annealing temperature of your PCR assay is one of the most critical parameters for reaction specificity. The melting point of the primer sets the upper limit on annealing temperature. The NEB Tm Calculator should be used to determine the annealing temperature when using this enzyme.
During the cooling (annealing) phase of PCR, the primer binds to the target and initiates copying of the target DNA/RNA sequence. For greater accuracy, optimize the annealing temperature by using a thermal gradient. 3 Identification the location of the target sequence in the DNA template Primer design and primer specificity PCR optimization Post-PCR analysis results using agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE) PCR troubleshooting Start your PCR and visualize.
The only cetrtain way is to run a gradient pcr at different annealing temperatures because Ta is variable and primer sets will often work well at. PCR involves the following three steps:. In this annealling step the temperature is much lower, allowing the primers to bind to the single-stranded DNA template (Figure:.
PCR- Optimization of Annealing Temperature. Three-step PCR includes denaturation, annealing, and extension steps. First, the genetic material is denatured, converting the double stranded DNA molecules to single strands.
Conversely, if T a is too high, reaction efficiency may be reduced because the likelihood of primer annealing is reduced significantly. The annealing temperature is determined by calculating the melting temperature (T m) of the selected primers for PCR amplification. Use the lowest primer T m when calculating the annealing temperature.
In the first step, denaturation, the DNA is incubated at 93–95°C from 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Thus, the annealing temperature chosen for a PCR depends directly on length and composition of the primer(s). Important instructions on calculating PCR annealing temperatures.
If the primer T m minus 5°C is close to the extension temperature (72°C), consider running a two-step PCR protocol. If the melting temperature of the primer (T m) is close to the extension temperature (72°C) or a few degrees lower, consider using a two-step PCR protocol that includes a denaturation step and a. The high percentages of false PCR products were obtained when PCR primers with a high melting temperature (Tm) were used at the annealing temperature of 55°C—primer 22 has the Tm of 84.1°C, and 75% of false PCR products were obtained with this primer;.
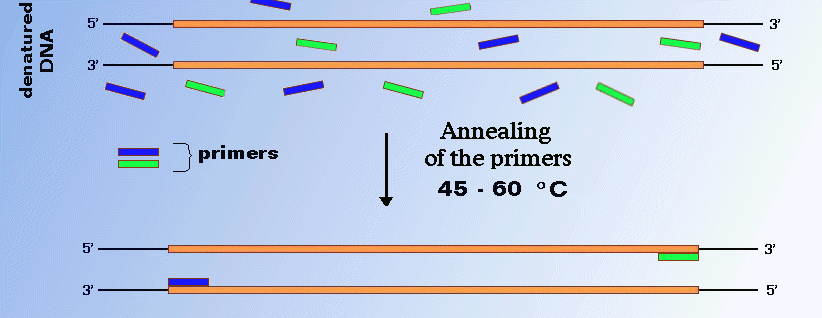
It is important to understand that the primers will bind (anneal)only to that segment of the template which contains a. Many online tools are freely available for primer design, some of which focus on specific applications of PCR. This is a typical temperature-dependent DNA :.
If temperature is too high the primers cannot anneal efficiently, and if the annealing temperature is too low the primers may bind nonspecifically They are present in large excess, so this step can be repeated a lot of times. The annealing temperature of this step should be determined from the melting temperature of the selected primers to help ensure specificity of primer binding and target amplification. This type of protocol should be used when the T m of the primers is lower than the extension temperature or is less than 68°C.
A temperature gradient. Setting the annealing temperature too low may lead to amplification of nonspecific PCR products. This can lead to nonspecific PCR amplification and will consequently reduce the yield of the desired product.
However, as the polymerase has some reduced activity between 45 and 65o C (interval in which most annealing temperature are chosen), longer annealing times may increase the likelihood of unspecific. On the other hand, setting the annealing temperature too high may reduce the yield of a desired PCR product. In the first step, two primers anneal at their respective 3' ends (step I in the figure).
GC content – The GC content of primers should be 35-65%. Touchdown PCR (Step-down PCR):. PCR annealing temperature a few degree (4-6) lower than the melting temperature is usually used to increase the probability of primer binding.
Good PCR primers strike a fine balance between specificity and amplification efficiency. The annealing temperature at the initial cycles is usually a few degrees (3–5 °C) above the T m of the primers used, while at the later cycles, it is a few degrees (3–5 °C. At lower temperatures, PCR primers can anneal to each other via regions of complementarity, and the DNA polymerase can extend the annealed primers to produce primer dimer, which often appears as a diffuse band of approximately.
Use the NEB Tm Calculator to estimate an appropriate annealing temperature when using NEB PCR products. Primer annealing is a critical step in polymerase chain reaction or PCR. That annealing temp should be 55C-60C for 3 step PCR and for primers with a higher Tm, e.g.
A general rule of thumb is to begin with an annealing temperature 3–5°C lower than the lowest T m of the primers. A primer dimer is formed and amplified in three steps. This specifies the minimal number of bases that the primer must anneal to the template at 5' side (i.e., toward start of the primer) or 3' side (i.e., toward end of the primer) of the exon-exon junction.
Optimal annealing temperatures will result in the highest product yield with the correct amplicon. In this step, the primers bind to flanking sequences of the target DNA for amplification. Primers are single strands of nucleic acids (synthetic oligonucleotides) that are necessary to initiate the PCR.
These single strands of DNA or RNA are specific and complementary to the target DNA/RNA sequence portion. On the melting temperature of the primer - template hybrid. The annealing temperature during a polymerase chain reaction determines the specificity of primer annealing.
DNA hybridization reaction and has to be optimized. Specificity is controlled primarily by primer length and annealing temperature. The annealing temperature used in conventional PCR is usually several degrees below the maximum at which primers can remain bound to template, to ensure stable binding.
Primers will anneal at all temperatures below the temperature that they fail completely. At temperatures just below this point, only very specific base pairing between the primer and the template will occur. In addition, PCR efficiency can be improved by additives that promote DNA polymerase stability and processivity or increase hybridization stringency, and by using strategies that reduce.
PCR involves a process of heating and cooling called thermal cycling which is carried out by machine. Gradient PCR for assay optimization is to determine the optimum annealing temperature (Ta) of the primers by testing identical reactions containing a fixed primer concentration, across a range of annealing temperatures. One should aim at using an annealing temperature (T a ) about 5°C below the lowest T m of the pair of primers to be used.
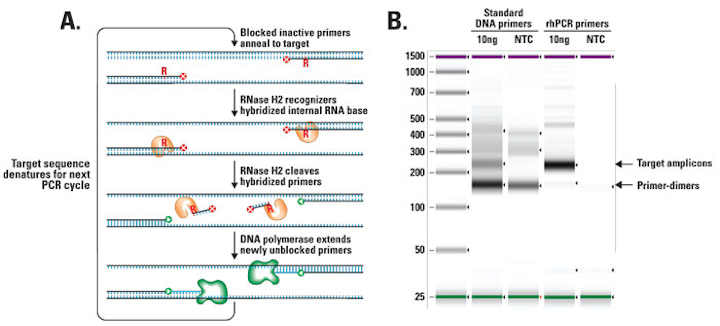
Because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a preexisting 3'-OH group, it needs a primer to which it can add the. Taq DNA Polymerase is the enzyme most widely used in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).The following guidelines will help ensure the success of PCR using New England Biolabs’ Taq DNA Polymerase for routine PCR. Hot-start PCR also can reduce the amount of primer-dimer synthesized by increasing the stringency of primer annealing.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of DNA. As the annealing temperature drops the primer can anneal to an increasing number of similar complementary. No PCR needs 2 primers working so both must anneal.
Test an annealing temperature gradient, starting at 5°C below the lower Tm of the primer pair;. To calculate melting temperature or for more. We can avoid most of these problems using primers of 15- nucleotides in length (note that the examples in the diagrams below use 5 nucleotide primers for simplicity – we would not use these in a real PCR.
Scorpions PCR primers contain a sequence complementary to an internal portion of the target sequence. The optimal annealing temperature for PCR is calculated directly as the value for the primer with the lowest Tm (T mmin):. Each of these steps requires incubation of the reaction mixture at different temperatures.
The annealing of the forward and reverse primer to the two strands of the target DNA is shown in figure 2. The optimal annealing temperature (T a Opt) for a given primer pair on a particular target can be calculated as follows:. Annealing – when the temperature is lowered to enable the DNA primers to attach to the template DNA.
The temperature is lowered to approximately 5 °C below the melting temperature (T m) of the primers (often 45–60 °C) to promote primer binding to the template. Where L is length of PCR fragment. Denaturation, Annealing and Extension.
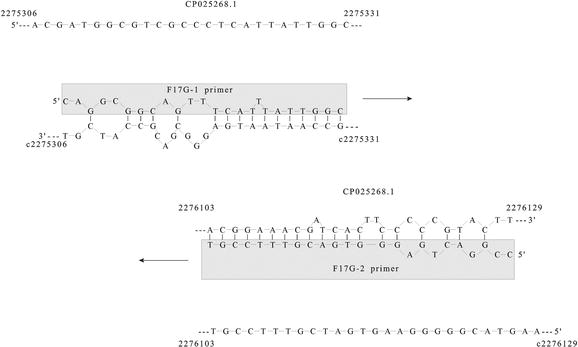
Where T m of primer is the melting temperature of the less stable primer-template pair, and T m of product is the melting temperature of the PCR product. Amplification of templates with high GC content, strong secondary structure, low concentrations or which produce products greater than 5 kb may require adaptation of these conditions. Primers F17G-1 and F17G-2 have the Tm of 72.4°C and 76.4°C, respectively, and 50% of.
The primers are then annealed to the complementary regions of the single stranded molecules. Optimal annealing temperatures for Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase tend to be higher than for other PCR polymerases. The PCR cycle involves three steps:.
Primers are short, made-to-order stretches of oligonucleotides that are synthesized in various lengths. Computer simulations of theoretical PCR results (Electronic PCR) may be performed to assist in primer design by giving melting and annealing temperatures, etc. The annealing temperature should not exceed the extension temperature.
There are three main stages:. Check specific product literature for recommended primer design;. The primer and Mg 2+ concentration in the PCR buffer and annealing temperature of the reaction may need to be optimized for each primer pair for efficient PCR.
Annealing Of Primers

What Is Pcr Polymerase Chain Reaction Facts Yourgenome Org

Polymerase Chain Reaction The Sciency Fellow

Pcr Primer Analysis Primer Analysis Primers Pcr Primer Sequence Medicilon Inc
Introduction To Pcr Primer Probe Chemistries Lsr Bio Rad

Order The Events That Occur In One Cycle O Clutch Prep
Uomustansiriyah Edu Iq Media Lectures 6 6 17 11 27 05 55 12 Pm Pdf
h5425 Molecular Biology And Biotechnology
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsa0m9qat5jhmwwqaeumw9ydjzrh6ow8yuouselzoct6porpume Usqp Cau

Working With Pcr

Merritt Genomics

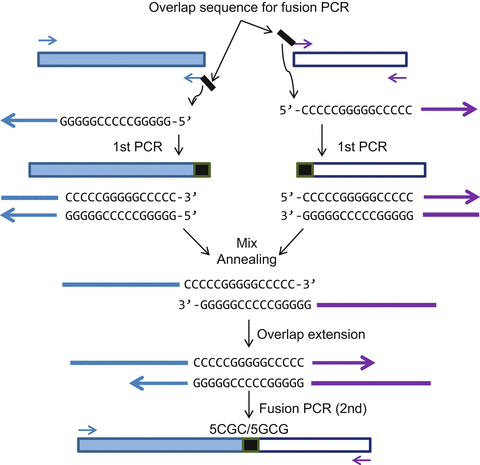
Pcr Overlap Extension Openwetware

Fastpcr Manual
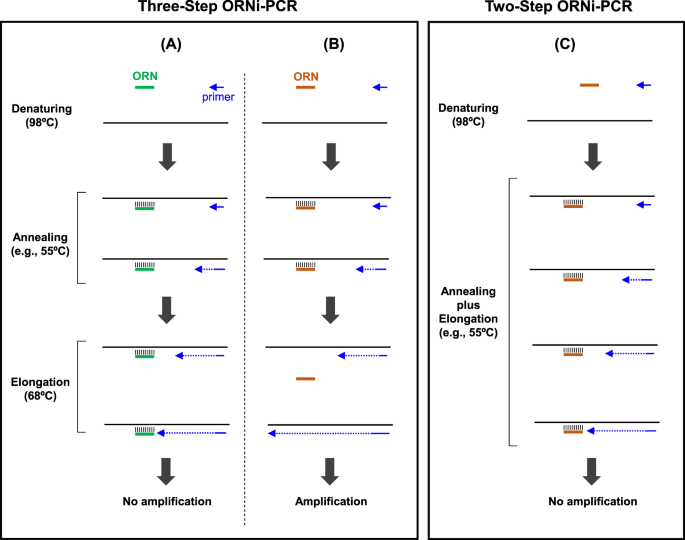
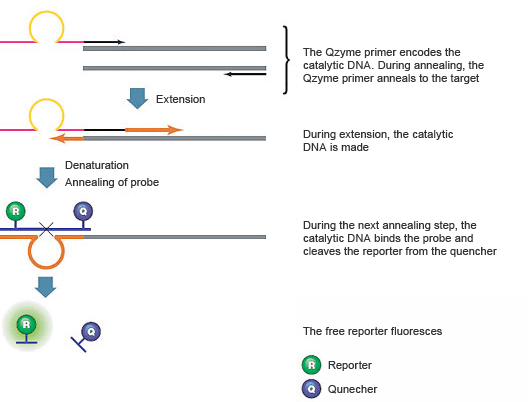
A Refined Two Step Oligoribonucleotide Interference Pcr Method For Precise Discrimination Of Nucleotide Differences Scientific Reports

Addgene Protocol How To Design Primers

Four Tips For Optimizing Your Pcr Amplification
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqzninymvxcoxl6ityd4zga 5jbhu67honfuwvj3pcas6qidmae Usqp Cau

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr

Minimal Primer Concentration Vs Minimal Pcr Annealing Time
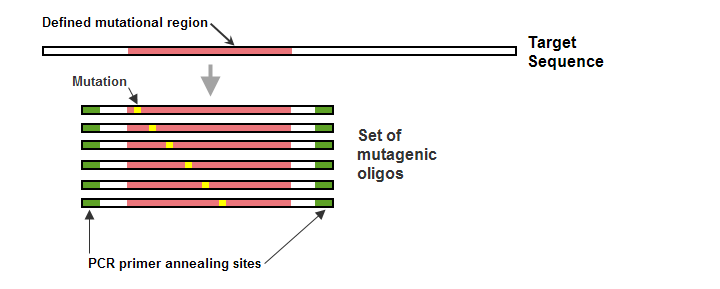
Overview Of Working With Mutagenesis Oligo Sets

Annealing Temperature Of 55 C And Specificity Of Primer Binding In Pcr Reactions Intechopen

Ngs Dna Library Clean Up Nvigen
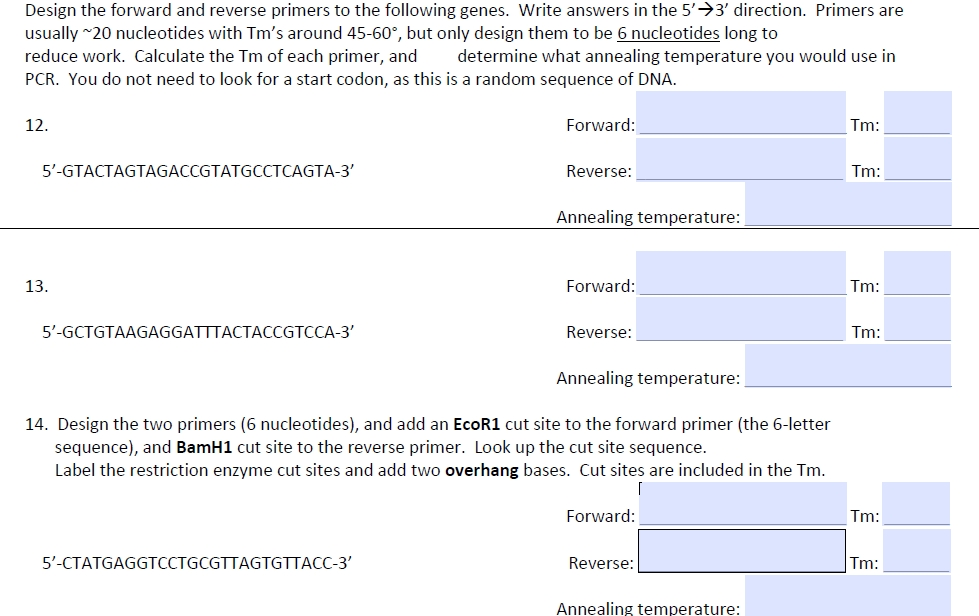
Solved Design The Forward And Reverse Primers To The Foll Chegg Com

Pcr Overview Goldbio

Pcr Steps Involved In Polymerase Chain Reaction Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
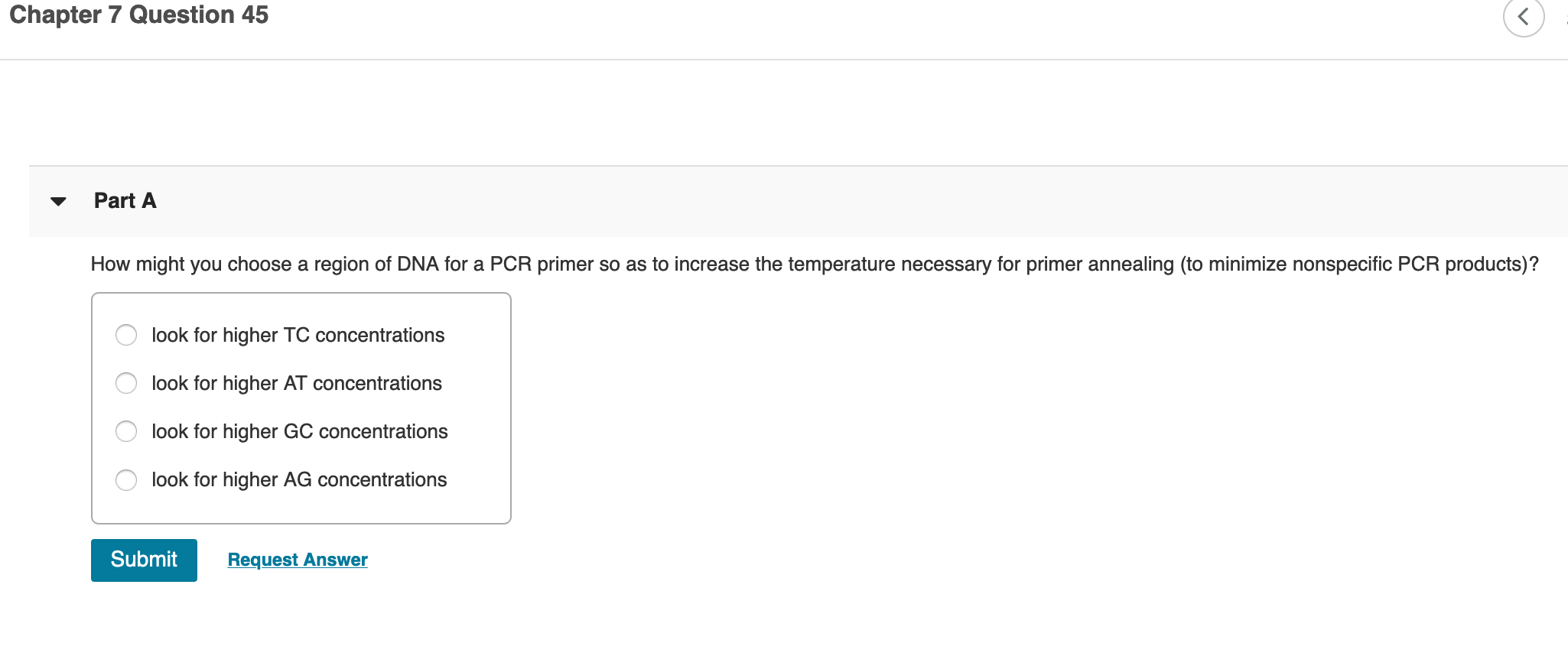
Solved Chapter 7 Question 45 Part A How Might You Choose Chegg Com
%20PCR%20works_big.png)
Rt Pcr Reverse Transcription Pcr Sigma Aldrich

Pcr Primer Design Guidelines
What Do You Mean By Pcr Quora

Fastpcr Manual
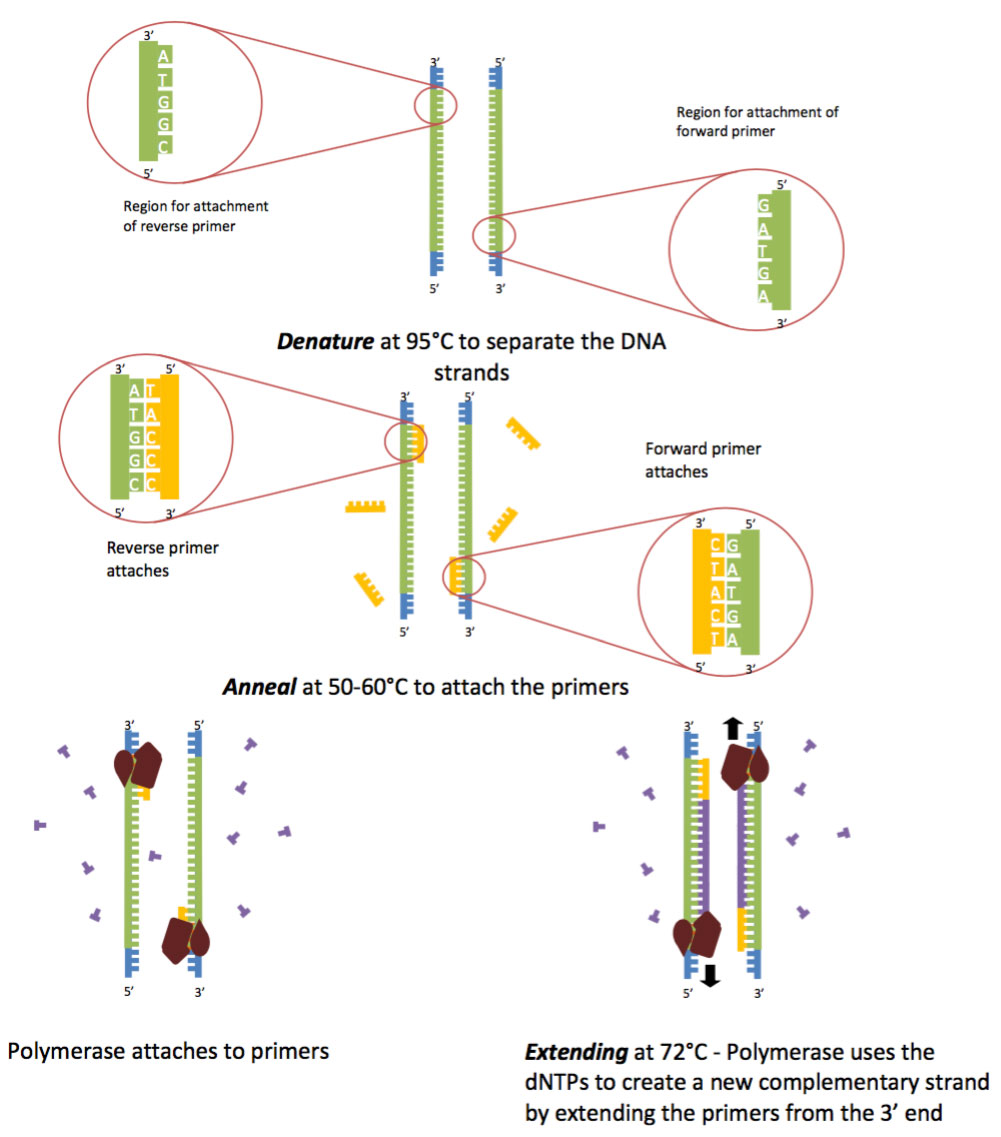
Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Diamantina Institute University Of Queensland

How Low Must Be The Annealing Temp Of The First Rounds For Overhang Pcr
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqksw6z5yfg9k6y7nfzbgoh65zaj7edursq Hmswh5zid18pniz Usqp Cau
Annealing Temperature Of 55 C And Specificity Of Primer Binding In Pcr Reactions Intechopen

Enhanced Ice Cold Pcr For The Sensitive Detection Of Rare
Ramping Up Pcr For Snp Genotyping Medical Laboratory Observer

Multiplex Pcr Optimization Myth Many Believe Dna Software

Pcr Basics Thermo Fisher Scientific Us

Merritt Genomics

Overhang Pcr
Minimum Gc Rich Sequences For Overlap Extension Pcr And Primer Annealing Springerlink

Qpcr Primer Design Revisited Sciencedirect

Pcr Overview Goldbio

Q Tbn 3aand9gcq01o1wjdexqqsg3cqqvkhhy9s9kgiuckveig Usqp Cau

Biohacking Pcr Primer H Media

Polymerase Chain Reaction The Sciency Fellow

Colony Pcr Pathways Over Time

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Diamantina Institute University Of Queensland
Annealing Temperature Of 55 C And Specificity Of Primer Binding In Pcr Reactions Intechopen

Pcr Primer Sizes And Annealing Temperatures Download Table
The Different Phases Of Pcr And Why They Are Important
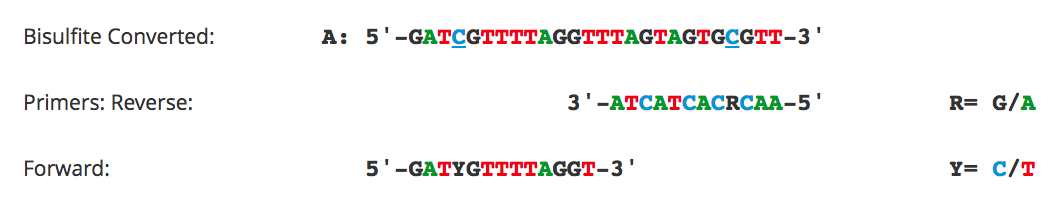
Bisulfite Beginner Guide

Annealing Temperature Of 55 C And Specificity Of Primer Binding In Pcr Reactions Intechopen
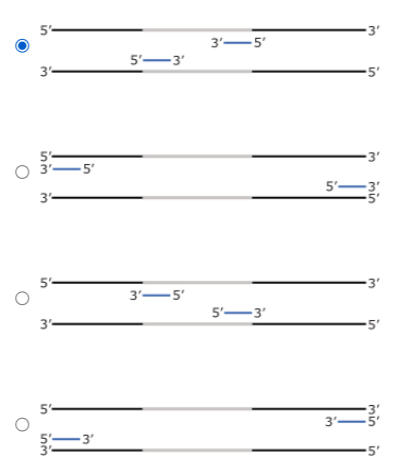
Answered Four Different Pairs Of Pcr Primers In Bartleby

The Reflex Workflow The Annealing Positions And Structure Of The Download Scientific Diagram
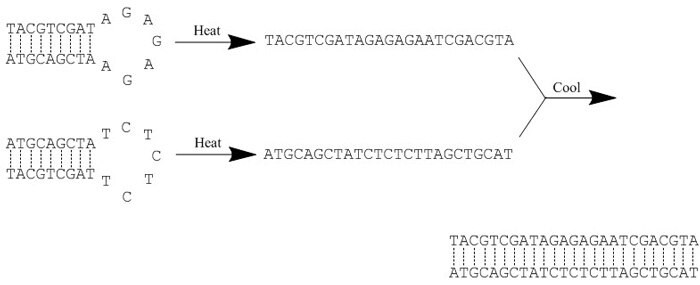
Protocol For Annealing Oligonucleotides Sigma Aldrich

Pcr Overview Goldbio

Rt Pcr Primers And Annealing Temperature Download Table
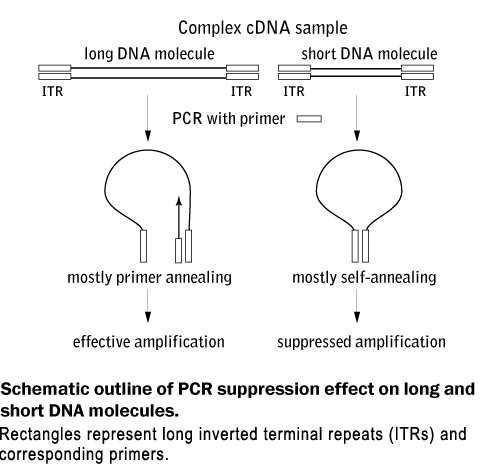
Evrogen Technologies Pcr Amplification Of Long Dna Fraction

Taq Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr

Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr

Pcr

A Novel Pcr Method Directly Quantifies Sequence Features That Block Primer Extension Biorxiv

Enhanced Ice Cold Pcr For The Sensitive Detection Of Rare

Platinum Ii Taq Hot Start Dna Polymerase Pcr Simplified With Universal Annealing Poster Technology Networks

How To Simplify Pcr Optimization Steps For Primer Annealing Thermo Fisher Scientific Us
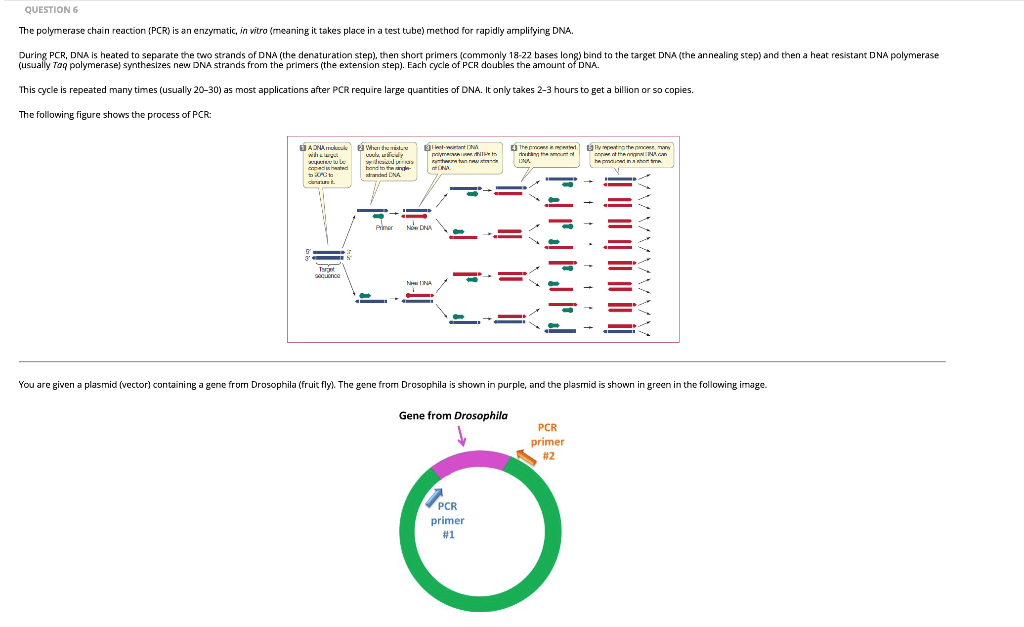
Solved Question 6 The Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Is Chegg Com

Rt Pcr Primers The Annealing Temperature Of The Rt Pcr Is Indicated Download Table
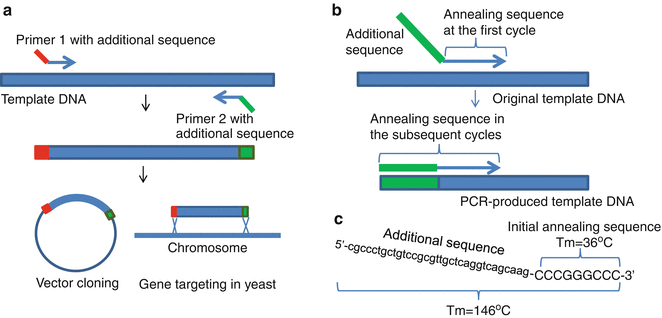
Minimum Gc Rich Sequences For Overlap Extension Pcr And Primer Annealing Springerlink
Www Qiagen Com Media Files Import Pdf En 1600 Maximizing Pcr And Rt Pcr Success Third Edition Ashx

Pcr Reaction Steps Of Pcr Viz Denaturation Annealing And Extension Pcr Primer Design Design Guidelines Primer Design

Variants Of Pcr Wikiwand
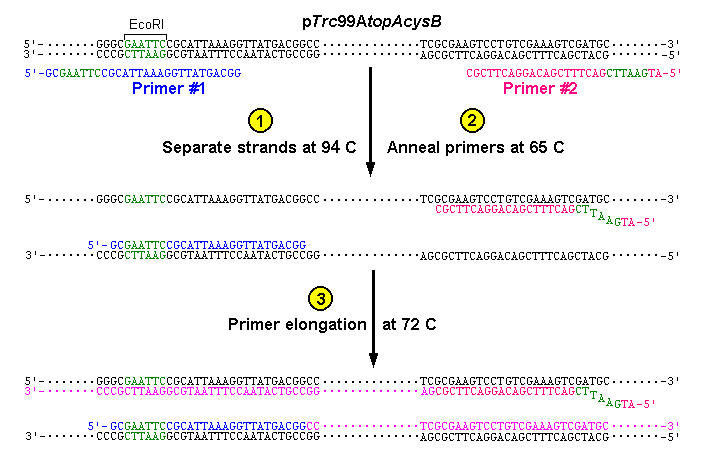
Learning Module Experiment 9a Biochemistry And Molecular Biology
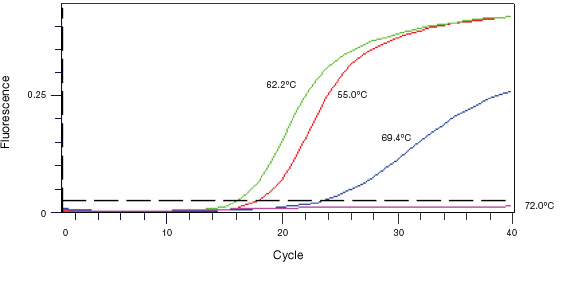
Qpcr Assay Design And Optimization Lsr Bio Rad

Pcr Primers Used In Rapd Pcr G C Content And Annealing Temperature Download Table

Pcr Primer Annealing Step Top Tip Bio

The Bumbling Biochemist S Guide To Pcr Polymerase Chain Reaction The Bumbling Biochemist

A Illustration Of Steps Involved In A Successful Pcr Reaction Download Scientific Diagram

Primer Based Approach For Pcr Amplification Of High Gc Content Gene Mycobacterium Gene As A Model
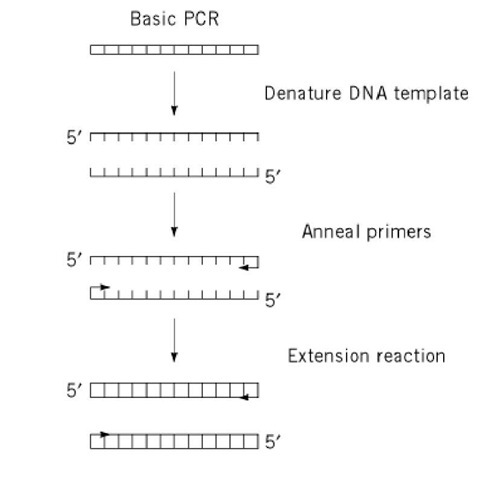
Polymerase Chain Reaction Molecular Biology
2
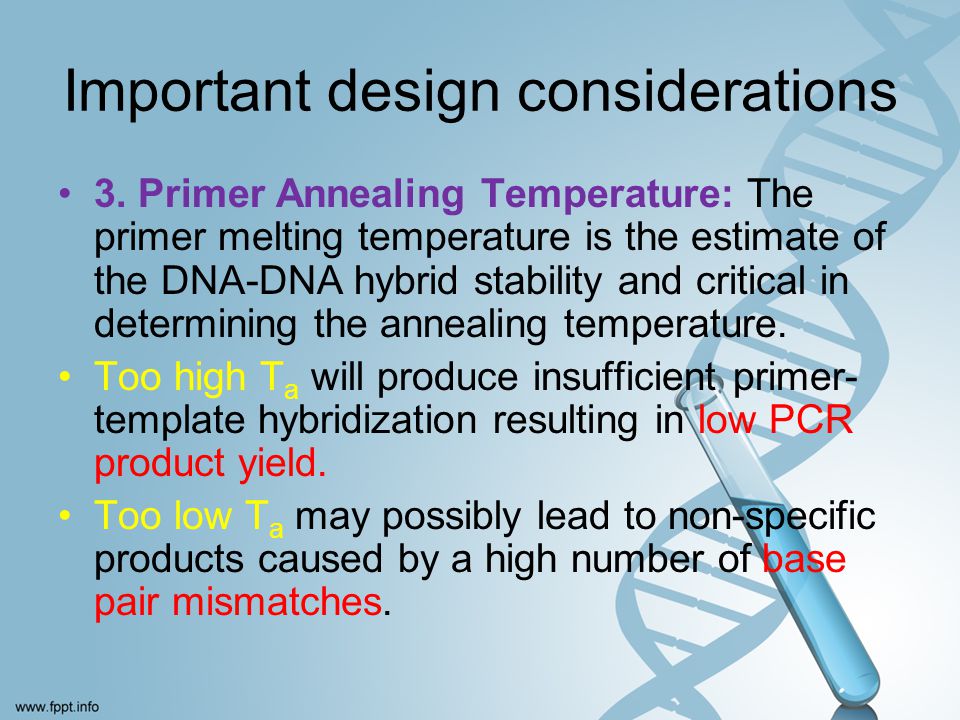
Pcr Primer Design Guidelines Ppt Download

Primers Used Primer Annealing Temperature T And The Pcr Product Sizes Download Table

Addgene What Is Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr

3 Basic Pcr Steps Of Dna Amplification Process Biology

Primer Designing Practical

Pcr Introduction Abm Inc

Pcr Overview Goldbio

Designing Forward And Reverse Primers To Have Matching Tm

Pcr Analysis An Examination National Diagnostics

Polymerase Chain Reaction Basic Protocol Plus Troubleshooting And Optimization Strategies Protocol

Primer Dimer Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs4odcmvxrqmgg1rkwiwzzmacyljwtbifdjap Tatc1xg7l Nli Usqp Cau

Polymerase Chain Reaction

What Is Needed To Amplify A Segment Of Dna

8 7 Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Biology Libretexts

Pcr



