From Earths Atmosphere Where Can The Carbon Atom Go Next

The Carbon Cycle Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

Carbon Cycle Wikipedia

Cold Light Astronomers Go To The Ends Of The Earth To See Cosmic Carbon
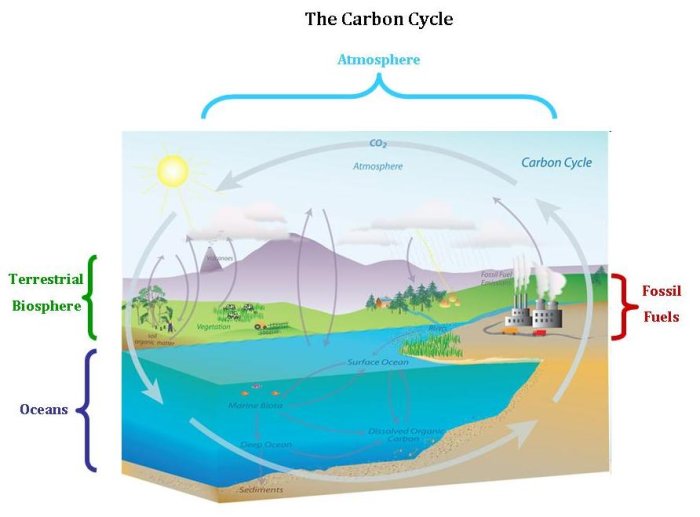
Carbon Cycle And Atmospheric Co2 Earth 530 The Critical Zone

A New Recipe For Hunting Alien Life Scientific American

How Can We Estimate The Mass Of The Atmosphere Oxford Interview Questions Explained University Of Oxford
One can go on and on about the uses and benefits of this important element.
From earths atmosphere where can the carbon atom go next. This carbon-containing solution is then. Carbon on Earth is found in the atmosphere, soil and rocks (the. 2 A caterpillar gets the.
A prominent atmospheric scientist Monday (Oct. A carbon atom could spend millions of years moving through Earth in a complex cycle. The carbon is used in sugar synthesis From the earth's atmosphere the carbon atoms go to the plants as their next destination.
Gas whose molecules contain 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms;. These atoms can be a part of both living things like plants and animals, as well as non-living things like water, air, and even rocks. The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere.
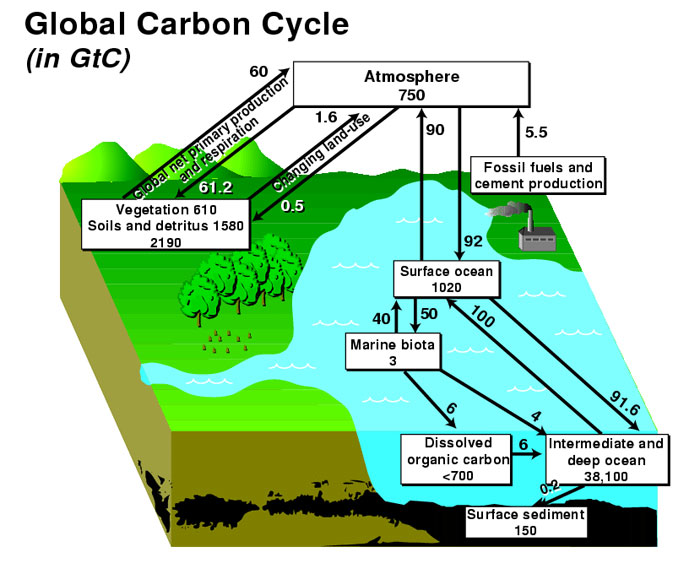
How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a plant?. Then, marine animals (biosphere) consume the plants and the carbon for energy. After rock, the ocean is the next biggest storage site with 38,000 billion tonnes of dissolved CO2.
The table also emphasizes the dissolution of atmospheric gases by the ocean. The fast carbon cycle is largely the movement of carbon through life forms on Earth, or the biosphere. Atmosphere to oceanic C02 to marine plants 2.
As such, it is important for us to know how Carbon present in various forms in the atmosphere, biosphere and lithosphere is exchanged between them and used. Carbon can exist in many different forms:. 1 A tree absorbs the carbon from the atmosphere into its leaves for photosynthesis.
Next, marine plants and algae (biosphere) use the CO2 to make glucose and oxygen. Measuring soil carbon can be challenging, but a few basic assumptions can make estimating it much easier. The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next.
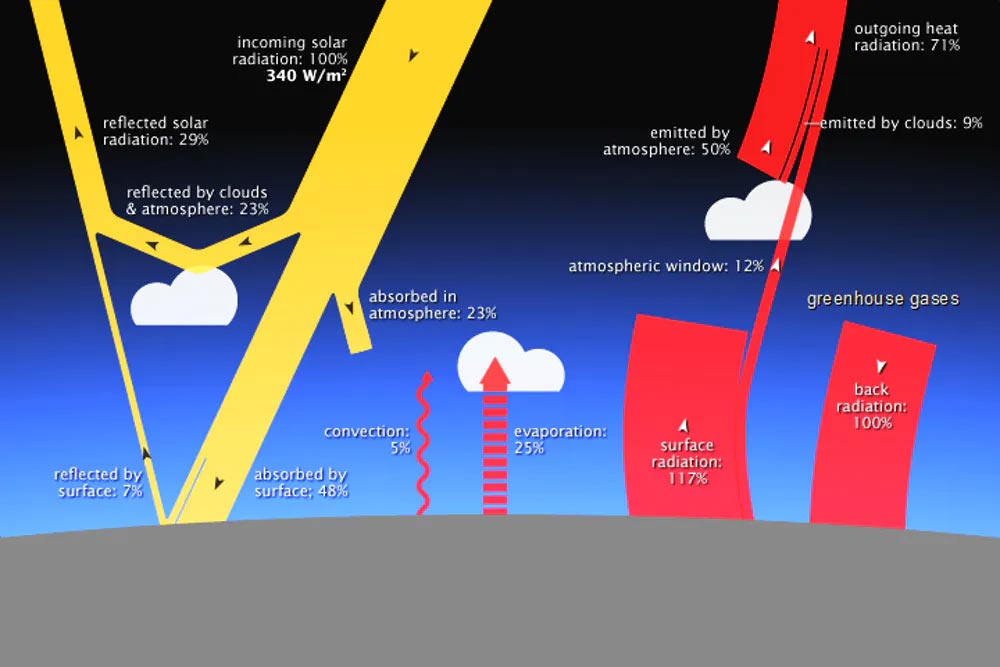
Click on Land plants and read the description. Can you find two ways that carbon can get from the ocean to the lithosphere?. Carbon dioxide and water vapor in atmosphere trap infrared radiation, re-reflecting it back toward earth.
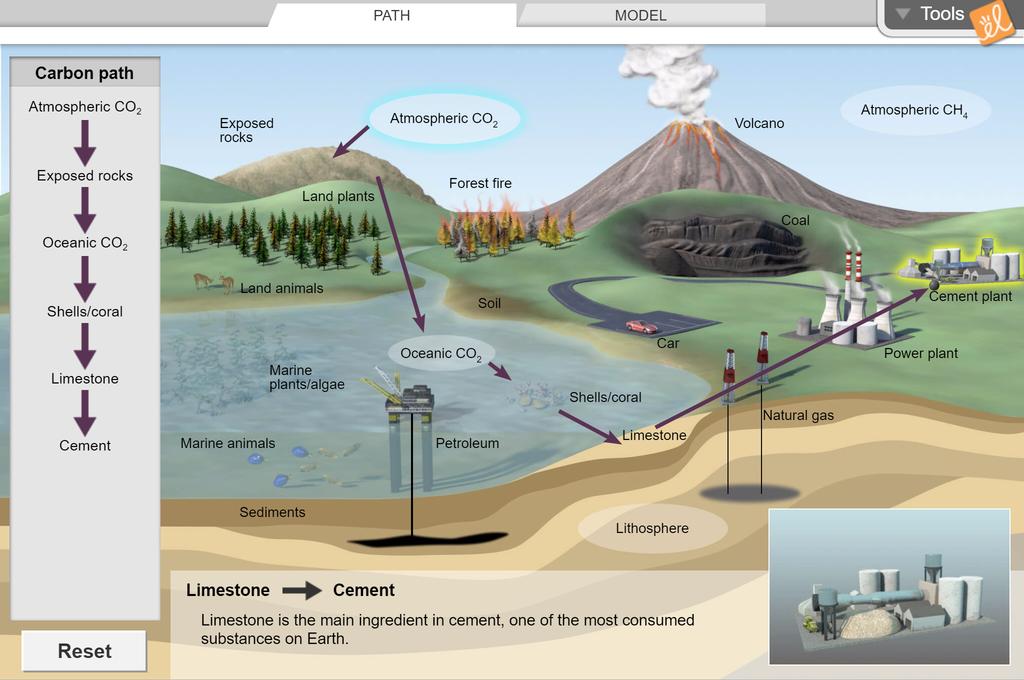
The global carbon cycle is a whole system of processes that transfers carbon in various forms through the Earth’s different parts. They got from the atmosphere to a plant by exposed rocks and the atmosphere. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO 2 area, highlighted in yellow.
The land plants, exposed rocks and the ocean. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO2area, highlighted in yellow. 99.9 per cent of carbon is stored in rock, mostly as limestone.
NOAA buoys measure carbon dioxide. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO 2 area, highlighted in yellow. Carbon can enter the atmosphere.
Click on Land plants and read the description. Lamont research professor David Goldberg and his colleagues, for example, are studying the feasibility of storing 50 million tons or more of CO2 in basalt. Carbon makes up Earth's plants and animals, and is also stored in the ocean, the atmosphere, and the crust of the planet.
Where the carbon is located — in the atmosphere or on Earth — is constantly in flux. Most of Earth’s carbon is stored in rocks and sediments. All carbon eventually passes through the atmosphere.
From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the c…. How did the carbon atom get from the. The carbon atom can go to the ocean.
From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go next?. Using the Gizmo, find a carbon atom path from the atmosphere to the cement plant. It can regulate carbon because plants need it to live.
The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next. Although the temperature changes were touched off by variations in Earth’s orbit, the increased global temperatures released CO 2 into the atmosphere, which in turn warmed the Earth. These are the reservoirs through which carbon cycles.
But if the ocean stops absorbing the excess CO2, and instead releases more from the deep sea, that spells trouble. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the c…. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO2area, highlighted in yellow.
Gizmo Warm-up The Carbon Cycle Gizmo™ allows you to follow the many paths an atom of carbon can take through Earth’s systems. The movement of carbon from the atmosphere to the lithosphere (rocks) begins with rain. Where did all the Earth’s carbon come from?.
Levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere have corresponded closely with temperature over the past 800,000 years. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go next?. Carbon dioxide is called a greenhouse gas because it can trap some of the sun’s heat in the atmosphere.
From the icehouse to the greenhouse M ost of the carbon in nature is locked up in rocks and marine sediments. From the atmosphere the carbon atom gets into the oceans through absorption or plants through photosynthesis. Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment, the amount of carbon in this system does not change.
Carbon is also the key ingredient of fossil fuels, petroleum, is used in Carbon-dating, etc. The process involves pumping air from the atmosphere through a chamber containing sodium hydroxide, which reacts with the CO 2 to form sodium carbonate. Click on Land plants and read the description.
Antarctic ice-core data show the long-term correlation until about 1900. One classical thermal escape mechanism is Jeans escape, named after British astronomer Sir James Jeans, who first described this process of atmospheric loss. Collectively, the Earth’s plants store approximately 560 PgC, with the wood in trees being the largest fraction.
How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a. Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO2) is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the c….
A carbon atom could start in the atmosphere and it could dissolve in the cold waters in the surface of the ocean (hydrosphere). The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next. The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next.
To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the. Soil stores three times as much carbon as all the world's plants. For example, the processes that move carbon from the ocean (hydrosphere) to the lithosphere happen over a very large spatial scale and can take timescales of millions of years.
Wood is dense and trees can be large. The rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms. Argon and carbon dioxide make up most of the other 1%.
To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO 2 area, highlighted in yellow. How do plants on Earth affect the amount of carbon in Earth's atmosphere?. Journey of a carbon atom.
In the atmosphere, carbon exists mainly as carbon dioxide. The total amount of carbon in the world’s soils is estimated to be 1500 PgC. The carbon that is in the atmosphere in the form of CO 2 and CH 4 (methane) doesn’t stay in the atmosphere for long — it moves from there to other places and takes different forms.
The time it takes carbon to move through the fast carbon cycle is measured in a lifespan. Click on Land plants and read the description. The Paris Climate Agreement has set goals of containing warming to 1.5 to 2 degrees (Celsius) and we know pretty well how much carbon can be released to the atmosphere while keeping to that level.
To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO2area, highlighted in yellow. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the c…. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go next?.
One of the ingredients in cement is limestone.) Path:. Paths an atom of carbon can take through Earth’s systems. From Earth’s atmosphere,where can the carbon atom go next?.
The world’s oceans are one major potential sink, she said, absorbing carbon dioxide, changing it to other compounds containing carbon and locking it away from the atmosphere. Atmospheric carbon combines with water to form a weak acid—carbonic acid—that falls to the surface in rain. From earth's atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go to next?.
(The lithosphere is the rigid layer of the Earth, including the crust and part of the mantle.) 1. This helps to keep Earth warm. Water Vapor is the most common and provides over 80% of all warming Carbon dioxide is next in line with a 5% warming action and a concentration of 0.039% The rest are extremely rare in the.
Remaining gases are called trace gases because only small amounts of them are present. There are a few types of atoms that can be a part of a plant one day, an animal the next day, and then travel downstream as a part of a river’s water the following day. Oceanic C02 to atmosphere 2.
The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is in equilibrium with, and far less abundant than, the oceanic inventory of carbon dioxide, bicarbonate ions (HCO 3 −), and carbonate ions (CO 3 2−).If all carbon dioxide were somehow suddenly removed from the atmosphere, the ocean would replenish the supply within a few. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the Atmospheric CO2area, highlighted in yellow. The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next.
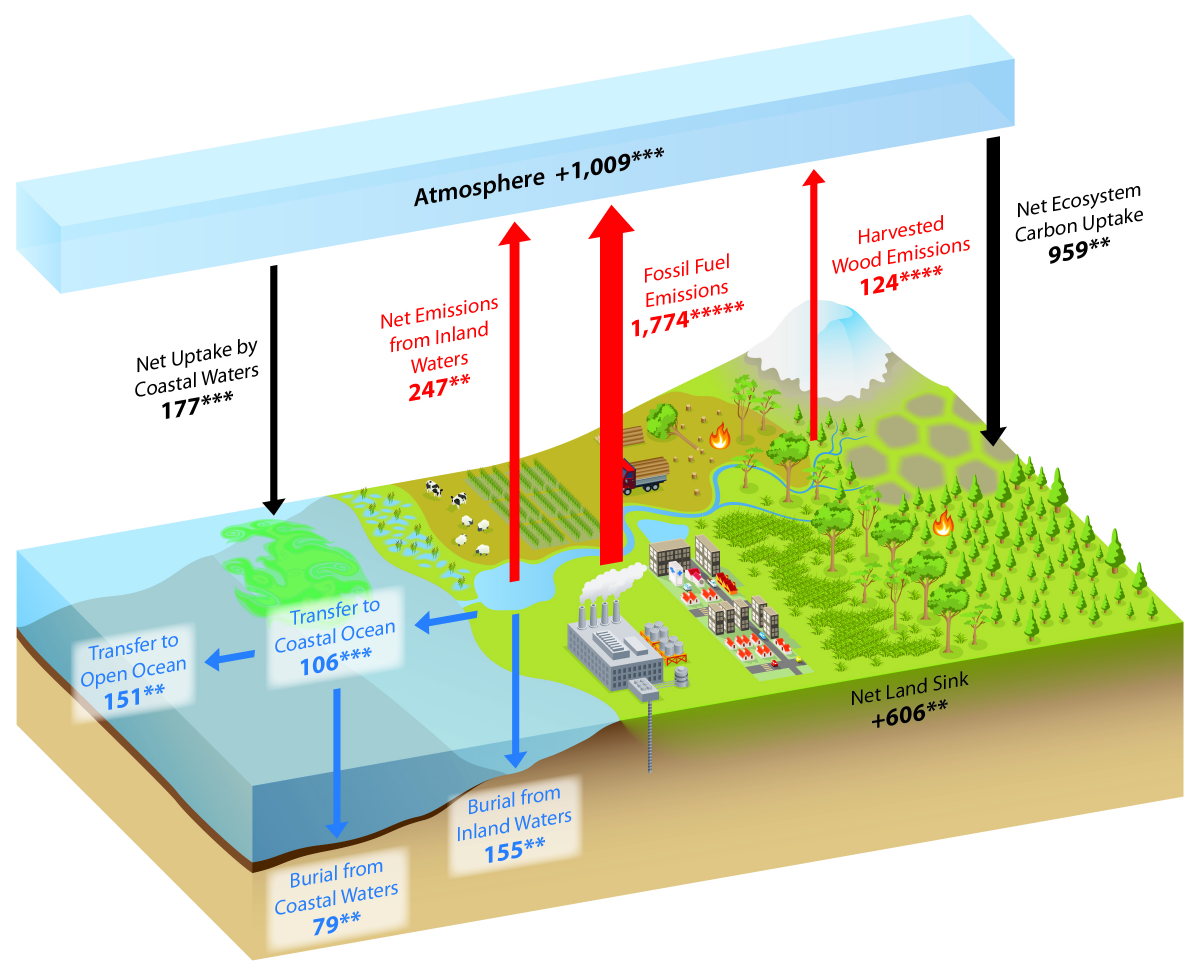
29) called for more research into natural carbon “sinks,” which today absorb almost half of man-made carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere and which will play a large role in determining the extent of future global warming. How did the carbon atom get. The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next.
How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a plant?. Carbon is found in carbon dioxide in the earth's atmosphere. How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a plant?.
It is a gas at standard temperature and. Click on Land plants and read the description. Area, highlighted in yellow.
Only a tiny fraction circulates in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO 2), where it acts as a thermostat for surface temperature through the so-called greenhouse effect. Sediments to lithosphere D. Think about a carbon atom that is released into the atmosphere from burning wood in a campfire.
Carbon's bonding with other elements result in more than 10 million different compounds, including calcium carbonate. The removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere can have a positive impact on global warming, in that the Earth is able to cool to a temperature which will no longer cause glaciers to melt. The atmosphere is one of the Earth's major carbon reservoirs and an important component of the global carbon cycle, holding approximately 7 gigatons of carbon.
The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from seashells to the atmosphere. BioTechSquad September 5, 16 September 9, 16 Uncategorized No Comments If you ask a geochemist, they might say that most of Earth’s carbon should have been burned off during the formation of the Earth or was chemically locked up in the core of our planet about 4.5 to 5 billion years ago.
The ways of returning carbon to the atmosphere are- 1. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go next?. Coal, natural gas and shale oil are mostly hydrocarbons and make up the majority of the earth's fossil fuels.
How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a plant?. The acid dissolves rocks—a process called chemical weathering—and releases calcium, magnesium, potassium, or sodium ions. The same atoms are recycled over and over in different parts of the Earth.
Scientists at the Earth Institute’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory have been working on carbon mineralization for several years, and are finding ways of speeding up the natural reaction to increase CO2 uptake and permanently store it. Atmospheric carbon plays an important role in the greenhouse effect.The most important carbon compound in this respect is the gas carbon dioxide (CO 2). Carbon is constantly on the move through the different components of Earth's Geosphere and Biosphere, but at very different timescales and spatial scales.
Without carbon dioxide’s natural ability to trap heat in the atmosphere, life as we know it could not exist. Essential to all forms of life other gases oxygen and nitrogen together make up 99% of dry air. As part of a carbon dioxide molecule, as coal, or as part of the body of a living organism, for example.
Jennifer's research highlights how carbon atoms move through living things, the atmosphere, and the Earth over tremendously long periods of time. In a quantity of gas, the average velocity of any one molecule is measured by the gas's temperature, but the velocities of individual molecules change as they collide with one another, gaining and losing kinetic energy. Between 10 15 and 10 17 grams (1,000 to 100,000 million metric tons) of carbon move through the fast carbon.
They release carbon in the atmosphere. It moves in and out of the atmosphere through the earth's regular carbon cycle.What it can not do is enter as pure carbon. The carbon cycle is a process where carbon is removed and returned to the atmosphere.
The colder the water is, the more CO2 can be dissolved. And read the description. The glowing blue areas represent possible locations the carbon atom could go next.
Atmospheric CO2 à Oceanic CO2 à Shells/coral à Limestone à Cement.

The Carbon Cycle Ucar Center For Science Education

Carbon Sink Wikipedia

Carboncyclese Docx Name Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero

Esa Timing Carbon Turnover

Valenti Eliana 12 2carboncycle Pdf Name Date Format Responses In Blue Bold Font Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Refer To Vocab File Course Hero
3

Unit 9 Reading

The Carbon Cycle Biology For Majors Ii

4 Construct Response
Static1 Squarespace Com Static e4b09a5adfc T 5ab03b7e2b6a28fdf Carboncyclese O 27brien Nb Pdf

Carbon Cycle Gizmo Docx Go To Www Explorelearning Com And Sign In Open The Carbon Cycle Gizmo Read The Instructions Carefully And Complete The Course Hero
The Atmosphere Getting A Handle On Carbon Dioxide Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet

Life On Venus Astronomers See Phosphine Signal In Its Clouds The New York Times
Planetary Science
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program

The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere Siyavula
Carbon Dioxide Is Warming The Planet Here S How Live Science

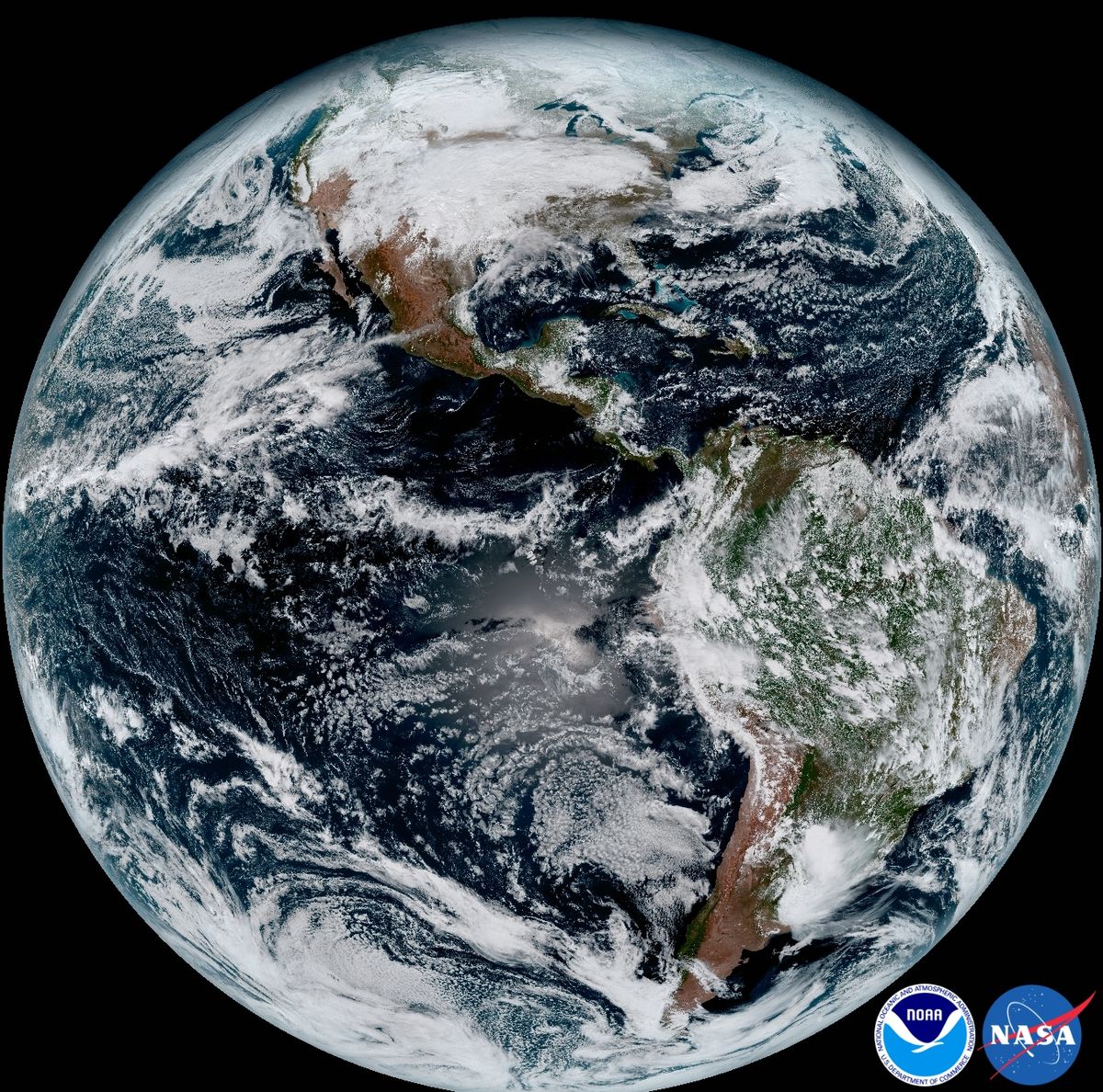
Peeling Back The Layers Of The Atmosphere Noaa National Environmental Satellite Data And Information Service Nesdis

What Is Carbon Dioxide c Bitesize

What Is Carbon Dioxide Drax

What Is Methane Methane Greenhouse Gas Facts
The Atmosphere Getting A Handle On Carbon Dioxide Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet

The Movement Of Carbon Around Earth S Atmosphere Explained Abc News

Lesson Plan Carbon Cycle Poster

The Carbon Cycle And The Nitrogen Cycle Earth Science
Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Answers Student Of Fortune

Carboncyclese Docx Name Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero
Www Stocktonusd Net Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 3232 Carboncyclese Pdf

Carboncyclese Docx Name Sade Wallace Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Course Hero
2
Assets Global Website Files Com 5beaf972d32c0c1ce1fa1863 5c79e67eeaea1d6994f037 Saildrone Antarctica Module2 Oa lesson1 Presentationnotes Pdf

Q Tbn 3aand9gcrsbpwuplv8d0jwbvzhokd9qhgyw3gyfb0nzq Usqp Cau

Carboncyclese Docx Name Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero
Science For Non Scientists Carbon Dating Student Environmental Resource Center

Atmosphere National Geographic Society
Http Www Pinemap Org Education Secondary Plt Carbon On The Move Draft Pdf

The Atmosphere
Carbon Cycle Gizmo Explorelearning
Www3 Epa Gov Airnow Teachers Rb Carboncycle Activity Pdf

Carbon Cycle National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration

Wait The Atmosphere Is Only 0 04 Carbon Dioxide How Does It Affect Earth S Climate
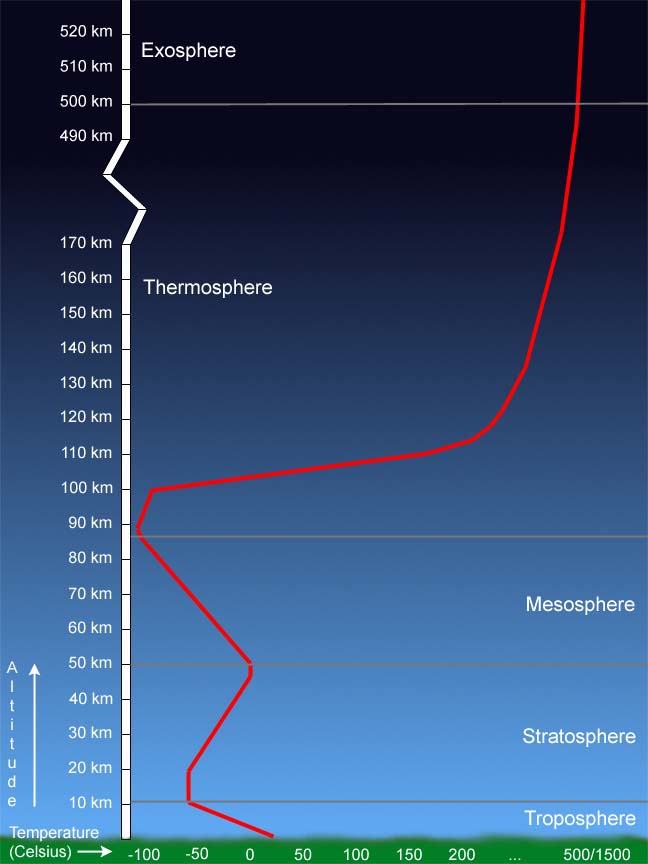
Layers Of Earth S Atmosphere

Wait The Atmosphere Is Only 0 04 Carbon Dioxide How Does It Affect Earth S Climate
Global Warming S Carbon Dioxide Changes Felt By Space Junk Space

Explainer Understanding Meteors And Meteor Showers Science News For Students
The Origin Of Life
The Atmosphere Getting A Handle On Carbon Dioxide Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet

Jrwfagfiv64m

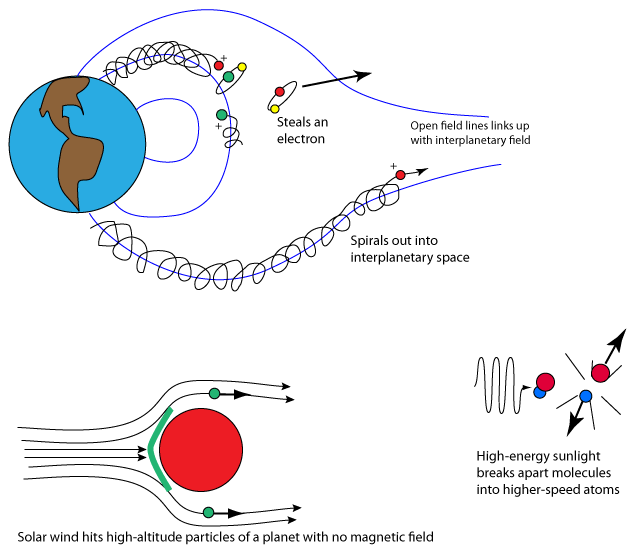
Loss Of Carbon In Martian Atmosphere Explained Nasa

Blast From The Past Carbon Cycle Story Georneys Agu Blogosphere

Chapter 6 Geochemical Cycles

The Ozone Hole Was Super Scary So What Happened To It Science Smithsonian Magazine

What Happens To Your Atoms After You Die The Immortal Infinite Journey Youtube

Where Did Mars Missing Carbon Go World Economic Forum
/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/33/6d/336ded1d-bf6f-4a2d-a676-d28ae0ad8ee4/artists_rendering_of_green_airglow_on_mars.jpg)
Green Glow Detected In Mars Atmosphere Smart News Smithsonian Magazine
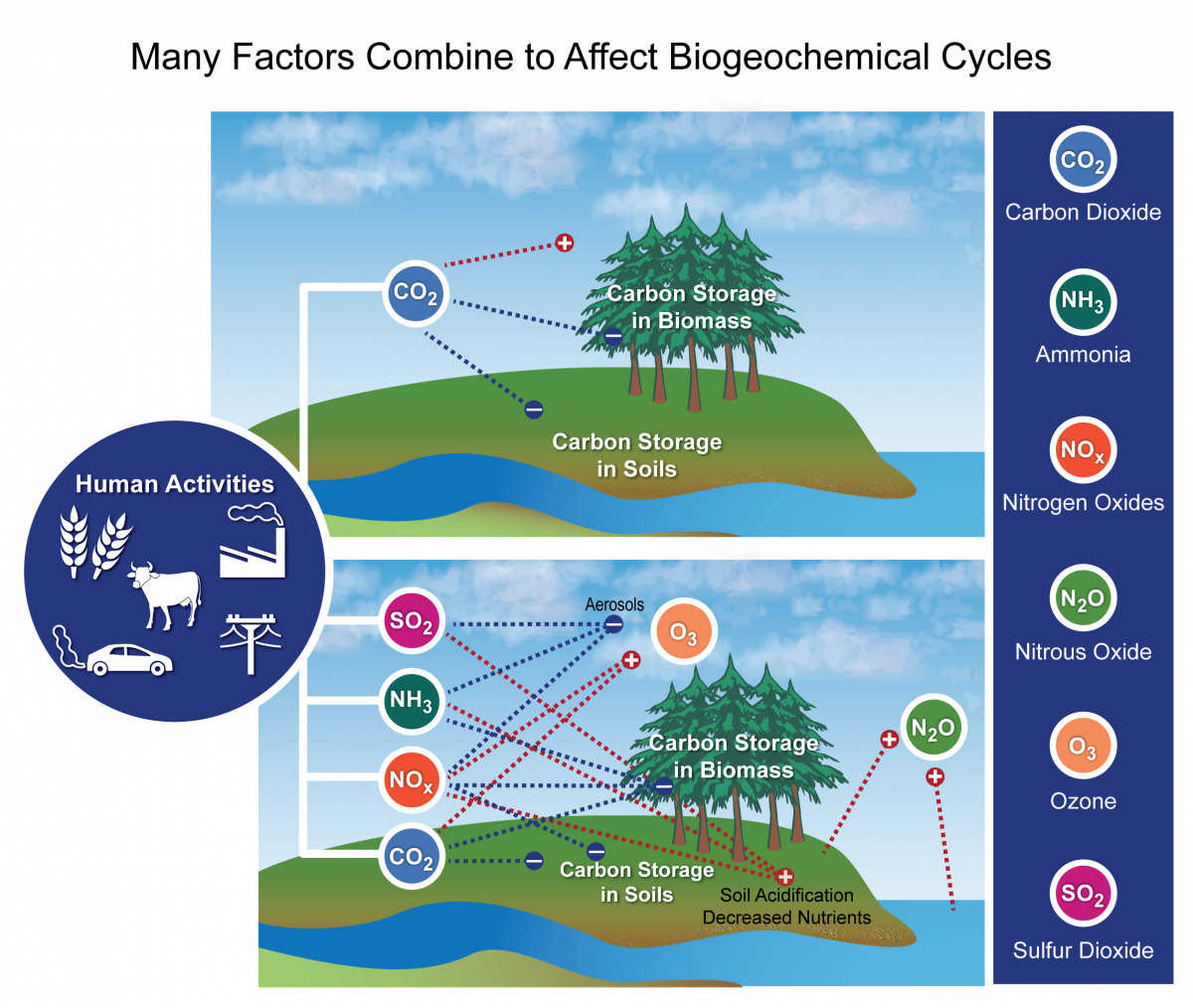
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program
Global Monitoring Laboratory Carbon Cycle Greenhouse Gases
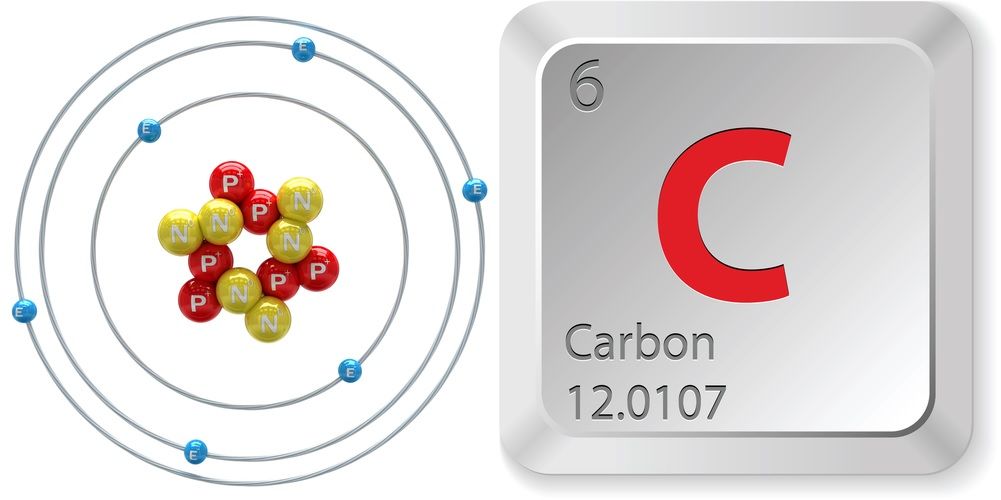
Carbon Element Facts Discovery Atomic Structure Uses Live Science

Wait The Atmosphere Is Only 0 04 Carbon Dioxide How Does It Affect Earth S Climate

Gizmos Carboncyclese Hc Pdf Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary U0b U0b Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero

Carbon Cycle Definition Steps And Examples Biology Dictionary
Http Www Sd162 Org Cms Lib011 Il Centricity Domain 522 Unit 5b packet 16 17 Pdf

Gizmos Carboncyclese Hc Pdf Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary U0b U0b Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero

2b The Global Carbon Cycle

Unit 9 Reading
3

Tracking Down The Carbon National Geographic Society
3

The Movement Of Carbon Around Earth S Atmosphere Explained Abc News

Lab 5 The Carbon Cycle
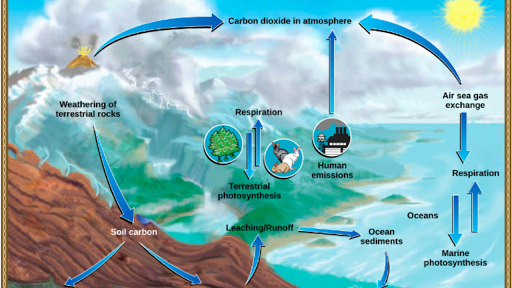
The Carbon Cycle Article Ecology Khan Academy

Atmosphere Of Earth Wikipedia

Earth S Atmosphere Composition Climate Weather Space

Earth S Atmosphere Stretches Out To The Moon And Beyond
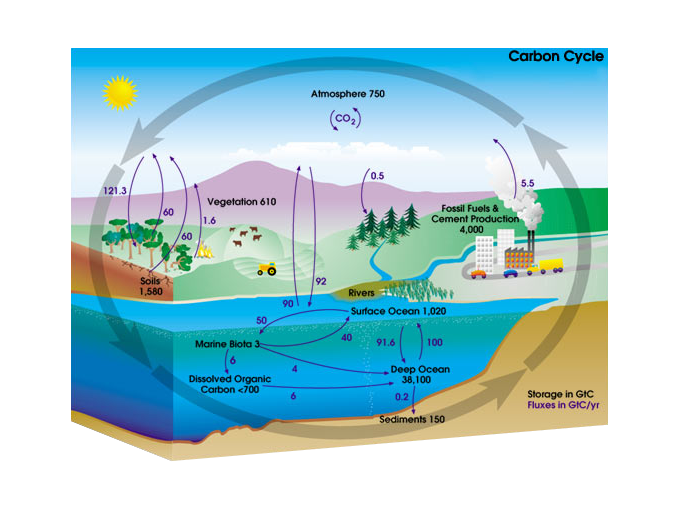
What Is The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis Decomposition Respiration And Combustion Earth How

Converting Trash To Valuable Graphene In A Flash Science News For Students

Carboncyclese Docx Name Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero

Carboncyclese Doc Name Angelina Hudson Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Course Hero

Carboncyclese Docx Name Maryann Armah Suriel Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Course Hero

Where Did Carbon Come From For Life On Earth Astrobiology

Carboncyclese Docx Name Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero
Static1 Squarespace Com Static e4b09a5adfc T 5ab03b7e2b6a28fdf Carboncyclese O 27brien Nb Pdf
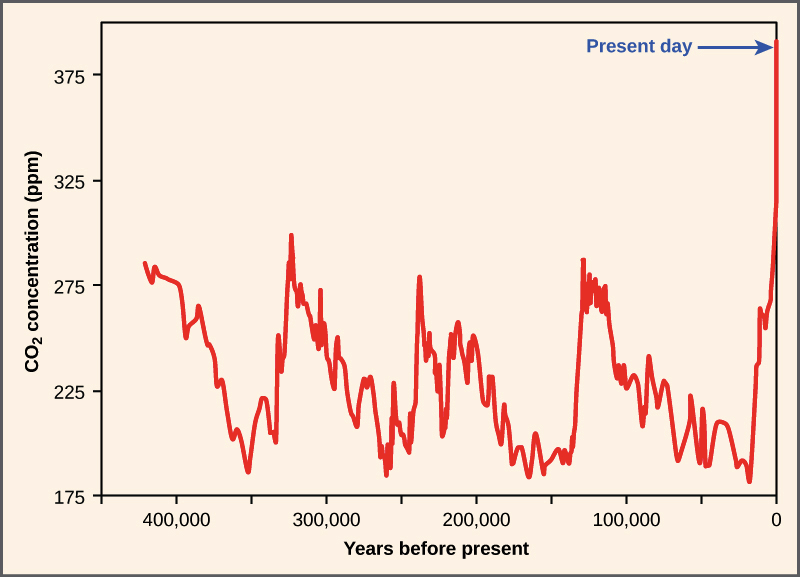
The Carbon Cycle Article Ecology Khan Academy

1a Trees The Carbon Storage Experts

What Is The Carbon Cycle

Carboncyclese Docx Carbon Dioxide In Earth S Atmosphere Carbon Cycle

The Archean Atmosphere Science Advances

Carboncyclese 1 Docx Name Date Student Exploration Carbon Cycle Vocabulary Atmosphere Biomass Biosphere Carbon Reservoir Carbon Sink Fossil Fuel Course Hero
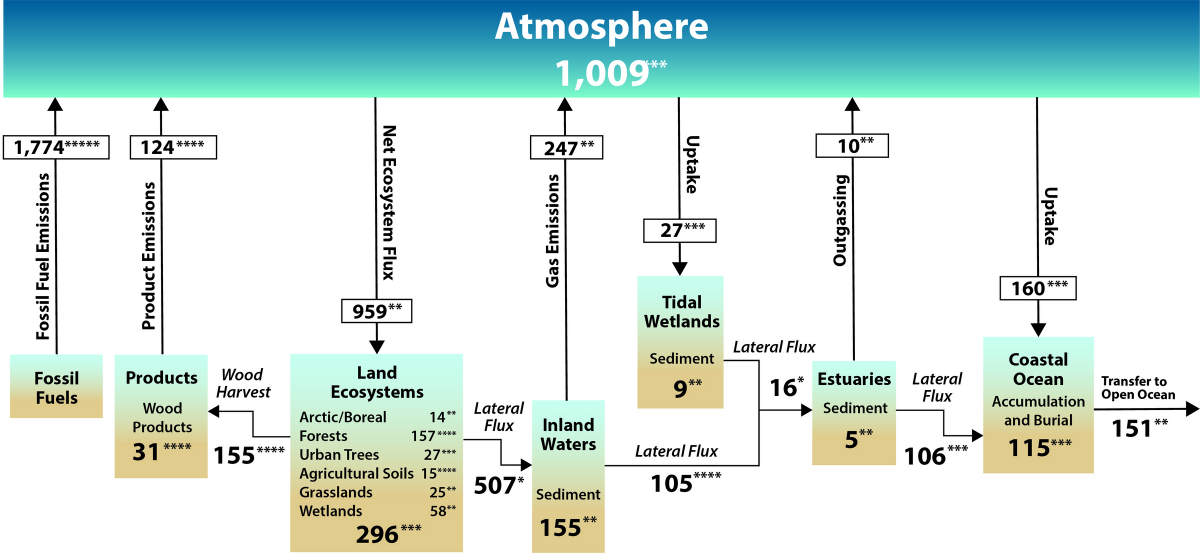
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19159489/co2.jpg)
Climate Change Pulling Co2 Out Of The Air Could Be A Trillion Dollar Business Vox
Www Nwf Org Media Pdfs Eco Schools 13 nasa 01 Module i Lesson 3 Follow The Carbon Atom 11 05 10 Ashx

Unit 9 Reading

The Ocean And The Carbon Cycle Science Learning Hub
3

Lesson Plan Carbon Cycle Role Play

Lab 5 The Carbon Cycle

6a Down To The Deep The Ocean S Biological Pump

The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids



